ISO 14001:2015 Environmental management system Certification Process in Nepal
ISO 14001:2015 is an internationally recognized standard for environmental management systems (EMS) developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). It provides a framework that helps organizations establish, implement, maintain, and improve their environmental performance. Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd. is here to shed light on the importance of ISO 14001 and guide you through the process of achieving certification.
What is ISO 14001, the Environmental Management System Standard?
ISO 14001 sets out the criteria for an effective environmental management system, enabling organizations to systematically address environmental concerns and improve sustainability.
It provides a framework that organizations can follow to minimize their environmental impact, comply with relevant regulations, and demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility.
What are the Main Objectives of ISO 14001?
The primary objectives of ISO 14001 are to help organizations:
a. Identify and understand their environmental aspects and impacts.
b. Establish and implement effective environmental policies and objectives.
c. Develop a systematic approach for monitoring, measuring, and improving environmental performance.
d. Comply with applicable legal and regulatory requirements.
e. Engage stakeholders and foster a culture of environmental awareness and responsibility.
Getting to the Heart of Why ISO 14001 is Important
ISO 14001 holds several key benefits for organizations:
a. Enhanced environmental performance: ISO 14001 helps organizations identify areas where they can reduce their environmental footprint, leading to improved resource efficiency and reduced waste generation.
b. Legal compliance: By implementing ISO 14001, organizations can stay up-to-date with environmental regulations and ensure compliance, minimizing the risk of penalties or legal issues.
c. Competitive advantage: Certification to ISO 14001 demonstrates an organization’s commitment to sustainable practices, which can enhance its reputation, attract environmentally conscious customers, and differentiate it from competitors.
d. Cost savings: Effective environmental management often leads to cost savings through improved resource utilization, waste reduction, and energy efficiency measures.
e. Stakeholder engagement: ISO 14001 encourages organizations to engage with stakeholders, including employees, suppliers, and local communities, fostering stronger relationships and building trust.
Key Changes in the Revised Standard of an Environmental Management System
The 2015 revision of ISO 14001 introduced several significant changes, including:
a. A stronger focus on leadership engagement and commitment.
b. Greater emphasis on the context of the organization and its specific environmental challenges.
c. Integration of the environmental management system into overall business processes.
d. Consideration of lifecycle thinking and supply chain management.
e. Enhanced requirements for risk-based thinking and continuous improvement.
Practical Steps to Becoming ISO 14001 Certified
Achieving ISO 14001 certification involves the following steps:
a. Gap analysis: Assess your organization’s current environmental management practices and identify areas that need improvement to meet ISO 14001 requirements.
b. Establishing objectives: Set clear environmental objectives and targets aligned with your organization’s context and goals.

c. Documentation and implementation: Develop the necessary documentation, policies, and procedures to support the implementation of ISO 14001 within your organization.
d. Training and awareness: Ensure that employees at all levels understand their roles and responsibilities in implementing the environmental management system.
e. Internal audit: Conduct internal audits to evaluate the effectiveness of your system and identify areas for improvement.
f. Certification audit: Engage an accredited certification body to perform an independent audit and assess your compliance with ISO 14001.
g. Continuous improvement: Continuously monitor and measure your environmental performance, learn from your experiences, and implement corrective actions to drive ongoing improvemen
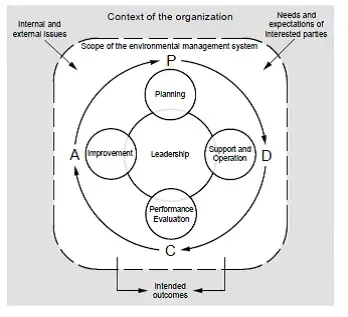
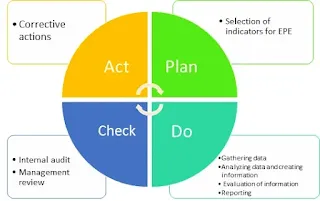
Plan-Do-Check Act Model for EMS ISO 14001
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) model is a systematic approach used in the ISO 14001 Environmental Management System (EMS) to drive continuous improvement. Here’s how the PDCA model applies to the implementation and maintenance of an EMS based on ISO 14001:
Plan:
- Establish the objectives and goals of the EMS based on the organization’s environmental policy.
- Identify the environmental aspects and impacts of your organization’s activities, products, and services.
- Define legal and other requirements applicable to the organization’s environmental performance.
- Develop plans and procedures to address identified risks, set targets, and establish action plans to achieve environmental objectives.
Do:
- Implement the plans and procedures developed in the planning phase.
- Communicate the environmental policy, roles, responsibilities, and expectations to employees and stakeholders.
- Provide appropriate training and awareness programs to employees regarding their roles in environmental management.
- Carry out operational activities in line with the established procedures and controls.
- Implement emergency preparedness and response procedures.

Check:
- Monitor and measure environmental performance through data collection and analysis.
- Conduct regular internal audits to assess compliance with the EMS and identify areas for improvement.
- Review the effectiveness of operational controls and identify any non-conformities.
- Evaluate performance against set targets, legal requirements, and objectives.
- Collect feedback from stakeholders, including customers, employees, and regulatory agencies.
Act
- Take corrective and preventive actions to address identified non-conformities and improve environmental performance.
- Review the effectiveness of corrective actions implemented and evaluate their outcomes.
- Update procedures, policies, and action plans based on the results of the review process.
- Continuously communicate and provide feedback to stakeholders on the organization’s environmental performance.
- Set new objectives and targets based on the review and improvement process.
The PDCA model should be applied iteratively and continuously to drive ongoing improvement in the organization’s environmental performance. By following this model, organizations can establish a culture of continual improvement, monitor environmental impacts, meet legal requirements, and achieve their environmental objectives effectively.
It’s important to note that the PDCA cycle is not a one-time process but rather a recurring cycle to ensure the EMS remains effective and aligned with the organization’s changing environmental context and requirements.
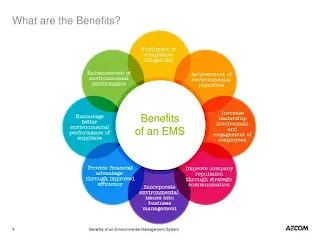
Environmental Management System -the business benefits
Implementing an Environmental Management System (EMS) offers numerous business benefits for organizations across various sectors. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of having an effective EMS:
- Improved Environmental Performance: An EMS helps organizations identify, monitor, and control their environmental aspects and impacts. By implementing sustainable practices and proactive measures, organizations can minimize their environmental footprint, reduce pollution, conserve resources, and enhance overall environmental performance.
- Compliance with Regulations: Complying with environmental regulations is a legal requirement for businesses. An EMS helps organizations stay up to date with applicable laws, regulations, and permits. By ensuring compliance, organizations can avoid penalties, fines, and legal issues that may arise due to non-compliance.
- Cost Savings and Efficiency: Implementing environmental practices that focus on resource conservation, waste reduction, and energy efficiency can result in significant cost savings. By optimizing resource usage, organizations can reduce energy consumption, minimize waste generation, and lower operating costs. Additionally, improved efficiency often leads to increased productivity and reduced material costs.
- Competitive Advantage: In today’s market, customers, and stakeholders increasingly value environmentally responsible organizations. Implementing an EMS and achieving certification, such as ISO 14001, demonstrates an organization’s commitment to sustainability, environmental protection, and social responsibility. This commitment can enhance an organization’s reputation, build customer trust and loyalty, and provide a competitive edge over competitors.
- Enhanced Stakeholder Relationships: An EMS fosters positive relationships with stakeholders, including employees, suppliers, customers, communities, and regulatory agencies. By engaging stakeholders in environmental initiatives, organizations can build trust, enhance collaboration, and establish mutually beneficial partnerships. Effective communication of environmental performance and initiatives strengthens stakeholder relationships and fosters a positive public image.

- Risk Management: An EMS helps organizations identify and manage environmental risks. By conducting risk assessments and implementing appropriate controls, organizations can proactively mitigate potential environmental incidents, accidents, and liabilities. Effective risk management not only protects the environment but also safeguards the organization’s reputation and financial well-being.
- Employee Engagement and Satisfaction: Implementing an EMS can boost employee morale and engagement. Employees are more likely to feel proud and motivated to work for an organization that prioritizes environmental responsibility. Involving employees in environmental initiatives, providing training opportunities, and recognizing their contributions to the EMS can improve job satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
- Access to New Markets and Customers: Many industries and sectors have specific environmental requirements or prefer to work with environmentally responsible partners. By implementing an EMS and achieving certification, organizations can access new markets, attract environmentally conscious customers, and secure contracts that require environmental compliance.
- Innovation and Continuous Improvement: An EMS encourages organizations to adopt a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. Through regular monitoring, measurement, and review of environmental performance, organizations can identify opportunities for innovation, implement best practices, and optimize their processes. This drive for improvement helps organizations stay ahead of emerging environmental challenges and adapt to changing market demands.
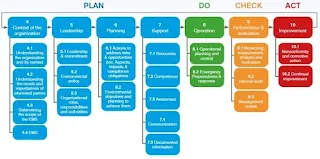
Requirements of ISO 14001- Clause by Clause explained
1. Scope
The scope clause in ISO 14001:2015 defines the boundaries and applicability of an organization’s Environmental Management System (EMS). It identifies the environmental aspects, activities, products, and services that are included within the scope of the EMS. The scope statement serves as a clear and concise description of the organization’s commitment to managing its environmental impact.
The scope clause typically includes the following elements: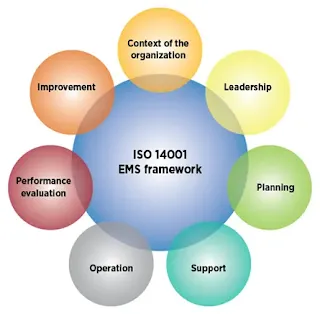
- Organization Identification: The scope clause starts by identifying the organization’s name, location, and any relevant subsidiaries or divisions covered by the EMS.
- Activities, Products, and Services: The clause specifies the activities, products, and services that are included within the scope of the EMS. This may involve describing the processes, operations, or sectors of the organization that are covered.
- Site Locations: If applicable, the scope clause may list the specific site locations or facilities that are included in the EMS coverage.
- Exclusions (If Any): In some cases, an organization may decide to exclude certain activities, products, services, or site locations from the EMS scope. These exclusions must be justified based on a thorough analysis of their environmental impacts and meet the requirements of ISO 14001.
- Applicable Requirements: The scope clause should specify the applicable legal and regulatory requirements related to the organization’s activities, products, and services. This ensures that the EMS considers and addresses all relevant environmental obligations.
The scope statement should be clear, concise, and aligned with the organization’s environmental policy and objectives. It provides a framework for the organization to define the boundaries of its environmental management efforts and sets the context for establishing environmental objectives, targets, and action plans.
It’s important to note that the scope of the EMS can be revised and expanded over time as the organization’s operations evolve or as new environmental considerations arise. Regular reviews of the scope clause are necessary to ensure its accuracy and relevance to the organization’s environmental management practices.
2. Normative Reference
The “Normative Reference” clause in ISO 14001:2015 specifies the relevant standards or documents that are cited as normative references within the context of the Environmental Management System (EMS). Normative references provide essential information that is necessary for understanding and implementing ISO 14001.
Within this clause, ISO 14001:2015 identifies the following normative references:
- ISO 9000: ISO 9000 is a set of standards that defines the fundamentals and vocabulary for quality management systems. ISO 14001 references ISO 9000 to establish common terminology and concepts used in both quality management and environmental management systems.
- ISO 14004: ISO 14004 provides guidelines for the implementation of an EMS. It offers practical advice on the application of ISO 14001 and assists organizations in developing and maintaining an effective environmental management system.
- ISO 14006: ISO 14006 provides guidelines for incorporating eco-design principles into the product development and design process. It assists organizations in considering environmental aspects throughout the entire life cycle of their products, leading to more sustainable and environmentally friendly outcomes.
- ISO/IEC 17021-1: ISO/IEC 17021-1 is a standard that specifies the requirements for bodies providing audit and certification of management systems. It outlines the criteria for competent and impartial auditing and certification bodies that assess organizations’ conformity to ISO 14001 and other management system standards.
The normative references listed in ISO 14001:2015 are crucial for understanding the principles, concepts, and guidelines related to environmental management systems. They provide additional guidance and context to support the effective implementation and certification of ISO 14001.
Organizations seeking to comply with ISO 14001 should refer to these normative references to ensure they have access to the necessary information and guidelines to successfully establish and maintain their EMS.
3 Terms and definitions
Here are the terms and definitions related to the Environmental Management System (EMS) standard, categorized according to their respective sections:
3.1 Terms Related to Organization and Leadership:
- Top Management: The person or group of people who direct and control an organization at the highest level and have the power to establish the organization’s policies and objectives.
- Environmental Policy: A documented statement of an organization’s commitment to environmental performance, including the prevention of pollution, compliance with applicable legal requirements, and the continual improvement of the EMS.

- Environmental Objective: A specific target set by an organization to achieve environmental improvement in line with its environmental policy.
- Environmental Aspect: An element of an organization’s activities, products, or services that can interact with the environment and potentially cause an environmental impact.
3.2 Terms Related to Planning:
- Environmental Impact: Any change to the environment, whether adverse or beneficial, wholly or partially resulting from an organization’s activities, products, or services.
- Legal and Other Requirements: The obligations stemming from laws, regulations, and other relevant provisions to which an organization subscribes, related to its environmental aspects.
- Environmental Risk: The potential adverse effects of an organization’s activities, products, or services on the environment, arising from its environmental aspects and their associated environmental impacts.
3.3 Terms Related to Support and Operation:
- Competence: The demonstrated ability to apply knowledge and skills to achieve the intended results.
- Documented Information: Information that is required to be controlled and maintained by an organization and can be in any format or medium.
- Operational Control: The process of implementing measures to manage an organization’s environmental aspects, including the establishment of procedures, work instructions, and training programs.
3.4 Terms Related to Performance Evaluation and Improvement:
- Monitoring: The systematic, planned, and ongoing activities to collect data on an organization’s environmental performance and its conformity to specified requirements.
- Non-conformity: The failure to meet a requirement specified in the EMS standard or any other applicable environmental management system requirement.
- Corrective Action: Action taken to eliminate the cause(s) of a detected non-conformity or other undesirable situation, preventing its recurrence.
These terms and definitions provide a foundational understanding of key concepts within the EMS standard. Familiarizing oneself with these terms is essential for effective communication, implementation, and compliance with the requirements of the EMS.
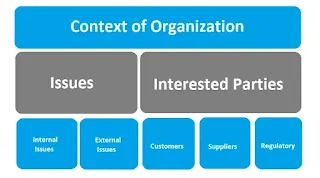
4. Context of the Organization
The “Context of the Organization” is a crucial aspect of ISO 14001:2015, which emphasizes the need for organizations to understand their internal and external environment. This understanding helps organizations shape their Environmental Management System (EMS) to be more effective and aligned with their objectives and stakeholders’ expectations. Here are key points related to the “Context of the Organization” in ISO 14001:
- Understanding the Organization and Its Context: Organizations are required to identify and comprehend the internal and external factors that can impact their environmental performance. Internal factors include the organization’s structure, culture, resources, and capabilities, while external factors encompass legal, regulatory, social, economic, and technological aspects. By understanding these factors, organizations can determine the scope and boundaries of their EMS and effectively manage environmental risks and opportunities.
- Identifying Stakeholders and Their Expectations: Organizations must identify the interested parties (stakeholders) that can affect or be affected by their environmental performance. These stakeholders may include employees, customers, suppliers, regulators, local communities, and NGOs. Understanding their expectations, concerns, and needs enables organizations to establish appropriate communication channels, engage stakeholders, and address their environmental requirements.

- Determining the Scope of the EMS: Based on their understanding of the organization and its context, organizations define the scope of their EMS. The scope statement outlines the boundaries of the EMS, including the activities, products, services, and site locations covered. This ensures that the EMS is comprehensive and focused on the relevant environmental aspects of the organization.
- Environmental Management System Integration: Organizations are encouraged to integrate the EMS into their overall business processes and management systems. This integration ensures that environmental considerations are considered in decision-making, planning, and operations. By aligning the EMS with the organization’s strategic direction, organizations can optimize their environmental performance and achieve their environmental objectives effectively.
- Compliance with Legal and Other Requirements: Organizations need to identify and understand the legal and regulatory requirements related to their environmental aspects. This includes keeping abreast of changes in environmental legislation and ensuring compliance with applicable requirements. Organizations must also consider other obligations, such as industry standards, codes of conduct, and voluntary initiatives, that are relevant to their environmental performance.
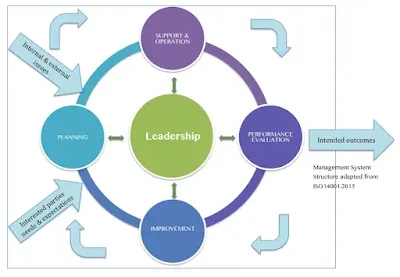
5. leadership
The leadership aspect in ISO 14001:2015 emphasizes the importance of top management’s involvement and commitment to the Environmental Management System (EMS). It highlights their role in establishing, implementing, and maintaining the EMS within the organization. Here are key points related to leadership in ISO 14001:
- Environmental Policy: Top management is responsible for establishing an environmental policy that reflects the organization’s commitment to environmental performance and compliance. The policy should provide a framework for setting environmental objectives, prevention of pollution, and continual improvement. Top management ensures that the policy is communicated, understood, and implemented at all levels of the organization.
- Organizational Roles and Responsibilities: Top management defines the roles, responsibilities, and authorities within the organization to ensure effective environmental management. This includes appointing competent personnel responsible for implementing and maintaining the EMS. Clear lines of communication and accountability are established to facilitate the integration of environmental considerations into the organization’s operations.
- Employee Engagement and Awareness: Top management promotes employee involvement in environmental management and encourages their active participation. This includes providing appropriate training, resources, and opportunities for employees to contribute to the EMS. Top management fosters an organizational culture that values environmental responsibility and encourages employees to identify and suggest improvements in environmental performance.
- Strategic Environmental Planning: Top management integrates environmental considerations into the organization’s strategic planning processes. Environmental aspects and impacts are considered when establishing the organization’s strategic objectives and plans. This integration ensures that environmental performance goals are aligned with the organization’s overall direction and objectives.

- Allocation of Resources: Top management ensures that adequate resources, including human resources, technology, and finances, are allocated for the successful implementation and maintenance of the EMS. This includes providing necessary resources for training, infrastructure, and equipment to support environmental initiatives and achieve environmental objectives.
- Communication and Reporting: Top management establishes communication channels to ensure that relevant information regarding the EMS is effectively communicated both internally and externally. This includes sharing the environmental policy, objectives, and performance with employees, stakeholders, and interested parties. Top management may also communicate environmental achievements and challenges through appropriate reporting mechanisms.
- Management Review: Top management conducts periodic management reviews of the EMS to ensure its continued suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness. This review includes assessing the organization’s environmental performance, compliance status, and progress towards achieving environmental objectives. Management review meetings provide a platform for top management to make informed decisions and allocate resources for continual improvement.
By demonstrating leadership commitment and engagement, top management plays a pivotal role in driving the success of the EMS. Their active involvement in establishing environmental policies, allocating resources, promoting employee engagement, and integrating environmental considerations into strategic planning sets the foundation for achieving environmental objectives and continual improvement.
6. Planning
The “Planning” aspect in ISO 14001:2015 focuses on establishing a systematic approach to environmental management within an organization. It involves setting environmental objectives, determining actions to achieve them, and planning for potential risks and opportunities. Here are key points related to the Planning aspect in ISO 14001:
- Environmental Aspects: Organizations are required to identify and evaluate the environmental aspects of their activities, products, and services. Environmental aspects are elements of an organization’s activities that can interact with the environment and potentially cause environmental impacts. By identifying and assessing these aspects, organizations can prioritize their environmental management efforts and allocate resources effectively.
- Legal and Other Requirements: Organizations must determine and keep up to date with applicable legal and regulatory requirements related to their environmental aspects. Additionally, they need to identify any other voluntary commitments or industry standards they choose to adhere to. This information is crucial for organizations to ensure compliance and set their environmental objectives and targets.
- Objectives and Targets: Based on the identified environmental aspects and legal requirements, organizations establish measurable environmental objectives and targets. Objectives are the overall goals an organization aims to achieve, while targets are the specific performance requirements to meet those objectives. Objectives and targets should be consistent with the environmental policy, relevant to the organization’s significant environmental aspects, and aligned with legal requirements.
- Environmental Management Programs: To achieve the established objectives and targets, organizations develop environmental management programs. These programs outline the specific actions, responsibilities, and timelines for implementing the necessary environmental initiatives. Environmental management programs provide a roadmap for organizations to effectively manage their environmental aspects and drive continuous improvement.
- Resources, Roles, and Responsibilities: Organizations need to determine and provide the necessary resources, including personnel, training, technology, and financial resources, to support the implementation of their environmental management programs. Clear roles and responsibilities should be defined to ensure accountability and effective coordination among individuals and departments involved in environmental management.

- Risk and Opportunity Management: Organizations are required to identify and assess potential risks and opportunities related to their environmental aspects. This includes analyzing the likelihood and potential consequences of adverse environmental impacts as well as identifying opportunities for environmental improvement. By addressing risks and seizing opportunities, organizations can proactively manage their environmental performance and prevent or mitigate negative impacts.
- Emergency Preparedness and Response: Organizations need to establish and maintain procedures for responding to and managing environmental emergencies. These procedures should be designed to minimize harm to the environment, facilitate timely response, and restore normal operations as quickly as possible. Regular drills and exercises can help test and improve the effectiveness of emergency preparedness and response plans.
By emphasizing the planning aspect, ISO 14001 ensures that organizations take a proactive approach to environmental management. By setting objectives, assessing risks, and establishing management programs, organizations can effectively manage their environmental aspects, comply with legal requirements, and drive continuous improvement in their environmental performance.
7 Support
The “Support” aspect in ISO 14001:2015 focuses on providing the necessary resources, infrastructure, and support mechanisms to enable effective implementation and maintenance of an Environmental Management System (EMS). This section emphasizes the importance of establishing a supportive framework to achieve environmental objectives and targets. Here are key points related to the Support aspect in ISO 14001:
- Resources: Organizations need to ensure that the necessary resources are allocated to support the EMS. This includes providing adequate personnel, infrastructure, technology, and financial resources to implement environmental initiatives, conduct training, and drive continual improvement. By allocating resources appropriately, organizations can effectively manage their environmental aspects and meet their environmental objectives.
- Competence, Awareness, and Training: Organizations are required to identify the competencies necessary for personnel involved in the EMS and ensure they possess the required skills and knowledge. Training programs and awareness campaigns are implemented to enhance employees’ understanding of their roles and responsibilities in environmental management. By promoting competence and awareness, organizations can foster an environmentally conscious workforce that actively contributes to the EMS.
- Communication: Effective communication plays a crucial role in environmental management. Organizations need to establish internal and external communication processes to ensure the timely and appropriate flow of information. This includes communicating the organization’s environmental policy, objectives, and performance to employees, stakeholders, and interested parties. Transparent and open communication helps build trust, engagement, and collaboration in environmental initiatives.
- Documentation: ISO 14001 emphasizes the need for organizations to establish and maintain documented information related to the EMS. This includes creating procedures, work instructions, and records that provide evidence of the implementation and effectiveness of the EMS. Documentation ensures consistency, clarity, and traceability in environmental management practices, audits, and compliance assessments.

- Control of Documents: Organizations need to establish procedures to control the creation, approval, distribution, and revision of documents related to the EMS. This ensures that the latest versions of documents are available, accessible, and properly maintained. Document control helps prevent the use of outdated or incorrect information, reduces errors, and facilitates effective decision-making.
- Operational Control: Organizations are required to establish operational controls to manage their significant environmental aspects and prevent or reduce adverse environmental impacts. This includes defining and implementing procedures, work instructions, and guidelines to ensure that activities, products, and services are performed in an environmentally responsible manner. Operational controls help organizations minimize environmental risks and ensure compliance with applicable legal requirements.
- Emergency Preparedness and Response: Organizations must establish procedures for identifying potential environmental emergencies and develop plans to respond effectively. These plans include actions to prevent or mitigate environmental harm, minimize the impact of emergencies, and restore normal operations. By being prepared for environmental emergencies, organizations can minimize negative environmental consequences and protect the health and safety of employees and the surrounding community.
By addressing the support aspect, ISO 14001 ensures that organizations have the necessary resources, competence, communication, and control mechanisms in place to effectively implement and maintain their EMS. By fostering a supportive environment, organizations can drive engagement, compliance, and continual improvement in their environmental performance.
8. Operation
The “Operation” aspect in ISO 14001:2015 focuses on the implementation of the Environmental Management System (EMS) within an organization. It covers the operational activities that organizations undertake to achieve their environmental objectives and targets. Here are key points related to the operation aspect in ISO 14001: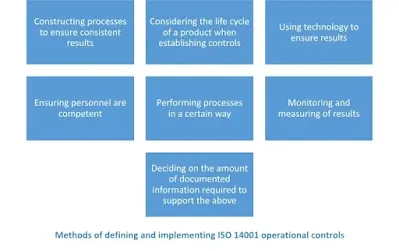
- Operational Planning and Control: Organizations need to establish and implement procedures and controls to manage their significant environmental aspects. This includes determining the criteria and methods for effective operational control, such as work instructions, training programs, and process documentation. By implementing operational controls, organizations can minimize adverse environmental impacts and ensure compliance with legal requirements.
- Emergency Preparedness and Response: Organizations must establish and maintain procedures to respond to environmental emergencies, such as spills, releases, or accidents. These procedures should include measures to prevent or mitigate harm to the environment, protect employees’ health and safety, and restore normal operations as quickly as possible. Regular testing and evaluation of emergency response plans help ensure their effectiveness.
- Outsourcing: If an organization outsources activities that can have significant environmental impacts, it needs to identify and control the associated environmental risks. This includes establishing criteria for selecting and evaluating contractors, communicating environmental requirements to contractors, and monitoring their environmental performance. By effectively managing outsourced activities, organizations can maintain control over their environmental performance.
- Monitoring and Measurement: Organizations are required to establish and maintain procedures for monitoring and measuring their key environmental performance indicators. This includes collecting and analyzing data related to significant environmental aspects, compliance with legal requirements, and the achievement of environmental objectives and targets. Monitoring and measurement help organizations assess their environmental performance and identify opportunities for improvement.
- Evaluation of Compliance: Organizations need to establish procedures for periodically evaluating their compliance with applicable legal and regulatory requirements. This includes monitoring changes in environmental legislation, conducting internal audits, and assessing the organization’s adherence to legal obligations. Compliance evaluations help organizations identify areas of non-compliance and take corrective actions to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Non-conformance and Corrective Action: Organizations must establish a process for identifying and addressing non-conformities related to their environmental performance. This includes investigating the root causes of non-conformities, taking corrective actions to prevent recurrence, and documenting the actions taken. By addressing non-conformities, organizations can improve their environmental performance and prevent future incidents.
- Control of Records: Organizations need to establish and maintain records to provide evidence of the implementation and effectiveness of the EMS. This includes creating, maintaining, and disposing of records in accordance with documented procedures. Records provide a documented history of environmental performance, compliance, and improvement efforts.
By focusing on the operation aspect, ISO 14001 ensures that organizations have the necessary procedures, controls, and monitoring mechanisms in place to implement their EMS effectively. By effectively managing their operations, organizations can minimize adverse environmental impacts, improve compliance, and work towards achieving their environmental objectives and targets.
9. Performance evaluation
The “Performance Evaluation” aspect in ISO 14001:2015 emphasizes the importance of monitoring, measuring, and evaluating an organization’s environmental performance. It involves assessing the effectiveness of the Environmental Management System (EMS), identifying areas for improvement, and demonstrating compliance with applicable legal and regulatory requirements. Here are key points related to the Performance Evaluation aspect in ISO 14001:
- Monitoring and Measurement: Organizations need to establish procedures for monitoring and measuring their key environmental performance indicators. This includes collecting data on relevant environmental aspects, such as energy consumption, waste generation, and emissions. Monitoring and measurement provide objective data to assess the organization’s environmental performance and identify trends over time.
- Evaluation of Compliance: Organizations must conduct regular evaluations to determine their compliance with applicable legal and regulatory requirements. This includes assessing whether the organization is meeting its legal obligations, permits, and licenses related to environmental aspects. Compliance evaluations help identify areas of non-compliance and facilitate corrective actions to ensure adherence to environmental regulations.

- Internal Audit: Internal audits are conducted to assess the overall effectiveness and conformity of the EMS. Trained auditors, either from within the organization or external to it, evaluate the EMS against the requirements of ISO 14001. Internal audits help identify areas for improvement, potential non-conformities, and opportunities for enhancing environmental performance.
- Management Review: Top management conducts periodic management reviews of the EMS to evaluate its continued suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness. Management reviews involve reviewing the organization’s environmental policy, objectives, performance, and the results of internal audits and compliance evaluations. These reviews enable top management to make informed decisions, allocate resources, and drive continual improvement in environmental performance.
- Non-conformance and Corrective Action: When non-conformities or incidents occur, organizations need to implement corrective actions to address the root causes and prevent their recurrence. Corrective actions may include process improvements, training, or changes in procedures to prevent similar incidents in the future. By taking corrective actions, organizations demonstrate their commitment to improving environmental performance.
- Continual Improvement: ISO 14001 encourages organizations to continually improve their environmental performance. This involves identifying opportunities for improvement based on the monitoring and evaluation of environmental performance indicators, compliance assessments, and internal audits. Organizations should establish mechanisms to capture and implement improvement ideas from employees, stakeholders, and interested parties.
- Communication of Results: Organizations are required to communicate their environmental performance, including achievements, goals, and areas for improvement, to relevant stakeholders. Communication may take the form of reports, newsletters, meetings, or other appropriate channels. Transparent communication helps build trust, engage stakeholders, and demonstrate the organization’s commitment to environmental responsibility.
By focusing on performance evaluation, ISO 14001 ensures that organizations regularly assess their environmental performance, compliance, and effectiveness of the EMS. By monitoring, measuring, and evaluating their performance, organizations can identify areas for improvement, implement corrective actions, and drive continual improvement in their environmental management practices.
10 Improvement
The “Improvement” aspect in ISO 14001:2015 emphasizes the importance of driving continual improvement in an organization’s environmental performance and the effectiveness of its Environmental Management System (EMS). It focuses on identifying opportunities for improvement, implementing corrective actions, and fostering a culture of innovation and sustainability. Here are key points related to the Improvement aspect in ISO 14001:
- Non-Conformance and Corrective Action: When non-conformities or incidents occur, organizations need to take corrective actions to address the root causes and prevent their recurrence. Corrective actions may include process improvements, training, or changes in procedures to prevent similar incidents in the future. By implementing corrective actions, organizations demonstrate their commitment to improving environmental performance.
- Continual Improvement: ISO 14001 encourages organizations to continually improve their environmental performance. This involves identifying opportunities for improvement based on the monitoring and evaluation of environmental performance indicators, compliance assessments, and internal audits. Organizations should establish mechanisms to capture and implement improvement ideas from employees, stakeholders, and interested parties.
- Environmental Performance Objectives and Targets: Organizations set environmental performance objectives and targets as part of their EMS. These objectives and targets should be measurable, consistent with the organization’s environmental policy, and aligned with legal requirements. By regularly reviewing and updating objectives and targets, organizations can drive improvement and track progress over time.
- Management Review: Top management conducts periodic management reviews of the EMS to evaluate its continued suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness. These reviews involve assessing the organization’s environmental performance, compliance, and the results of internal audits and corrective actions. Management reviews provide an opportunity to identify improvement opportunities, allocate resources, and drive continual improvement.

- Employee Engagement and Training: Engaging employees and providing them with appropriate training and awareness programs are vital for driving improvement. Employees at all levels of the organization should be encouraged to contribute ideas, suggestions, and innovations to enhance environmental performance. Training programs help build the necessary skills and knowledge to implement best practices and continually improve environmental management practices.
- Innovation and Sustainable Practices: ISO 14001 encourages organizations to embrace innovation and sustainable practices to improve their environmental performance. This may involve adopting new technologies, exploring alternative materials or energy sources, and implementing eco-friendly processes. By promoting sustainable practices, organizations can reduce their environmental impact and enhance their competitive edge.
- Communication and Stakeholder Engagement: Effective communication and engagement with stakeholders play a crucial role in driving improvement. Organizations should establish mechanisms to gather feedback, suggestions, and concerns from stakeholders regarding environmental performance. Open and transparent communication helps identify improvement opportunities, foster collaboration, and enhance the organization’s environmental credibility.
By emphasizing the Improvement aspect, ISO 14001 encourages organizations to foster a culture of continual improvement in environmental performance. By implementing corrective actions, setting objectives and targets, engaging employees, and promoting innovation and sustainability, organizations can drive positive change, reduce environmental impact, and achieve long-term sustainability goals.
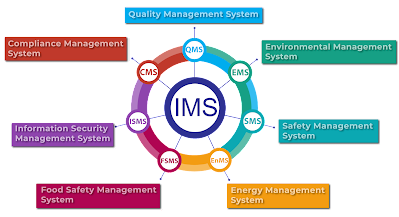
Integration with other management systems
Integration with other management systems is a key aspect of ISO 14001:2015, as it allows organizations to align their environmental management efforts with other established management systems within the organization. This integration can lead to improved efficiency, synergy, and effectiveness in achieving organizational objectives. Here are some key points regarding the integration of ISO 14001 with other management systems:
- Integrated Management Systems (IMS): Organizations often have multiple management systems in place, such as quality management systems (ISO 9001), occupational health and safety management systems (ISO 45001), or energy management systems (ISO 50001). Integrating ISO 14001 with these systems enables organizations to streamline processes, reduce duplication, and promote a holistic approach to managing environmental, quality, health and safety, and energy aspects.

- Common Framework: ISO management system standards, including ISO 14001, share a common high-level structure known as Annex SL. This structure provides a consistent framework for organizing the requirements of various management systems. By adopting a common framework, organizations can easily integrate the requirements, processes, and documentation of different management systems, facilitating their alignment and coherence.
- Risk-Based Approach: ISO 14001 emphasizes a risk-based approach to environmental management. Organizations can integrate this approach with other management systems, such as risk management systems (ISO 31000), to identify and manage risks that have both environmental and broader organizational implications. This integrated risk management approach helps organizations make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and address risks holistically.
- Documented Information: ISO 14001 requires organizations to establish and maintain documented information related to the EMS. This documentation can be integrated with other management system documentation to create a comprehensive repository of policies, procedures, work instructions, and records. Integrating documented information streamlines documentation control processes and ensures consistency across various management systems.
- Internal Audits and Management Reviews: Internal audits and management reviews are fundamental components of ISO 14001. Organizations can integrate these activities with audits and reviews conducted for other management systems. This integration allows for a comprehensive assessment of the organization’s performance across multiple dimensions, identifies synergies, and promotes an integrated approach to improvement.
- Objectives and Targets Alignment: Organizations can align the environmental objectives and targets established in ISO 14001 with the objectives and targets of other management systems. This alignment ensures that environmental considerations are integrated into broader organizational goals and strategies. It also facilitates coordinated efforts to achieve overall performance objectives while addressing environmental sustainability.
- Communication and Engagement: Integration with other management systems enables organizations to align their communication and engagement processes. This includes engaging stakeholders on environmental, quality, health and safety, and energy matters collectively, streamlining reporting processes, and providing a comprehensive view of the organization’s performance. Integrated communication enhances transparency, facilitates decision-making, and promotes a cohesive approach to stakeholder engagement.
By integrating ISO 14001 with other management systems, organizations can leverage synergies, improve efficiency, and enhance their overall performance. This integration enables organizations to address environmental aspects in conjunction with other organizational priorities, fostering a more comprehensive and sustainable approach to management.
Implementation of an EMS with IMS2 methodology
The implementation of an Environmental Management System (EMS) with IMS2 methodology involves the integration of multiple management systems into a cohesive framework. IMS2 stands for “Integrated Management System Stage 2,” which is a phased approach to implementing and managing multiple management systems within an organization. Here’s an overview of the implementation process using IMS2 methodology:
- Determine Scope and Objectives: Define the scope of the integrated management system, including the management systems to be integrated (e.g., ISO 14001, ISO 9001, ISO 45001, etc.). Establish clear objectives for the integrated system, aligning them with the organization’s overall goals and priorities.
- Conduct a Gap Analysis: Assess the existing management systems within the organization to identify commonalities, overlaps, and gaps. This analysis helps determine the areas where integration can be achieved and highlights any additional requirements needed to align with the IMS2 framework.
- Develop an Integrated Framework: Design a framework that outlines the structure and processes of the integrated management system. This framework should include policies, procedures, processes, and documentation that align with the requirements of the individual management system standards while ensuring consistency and compatibility.
- Establish Cross-Functional Teams: Form cross-functional teams representing different departments or areas responsible for each management system. These teams will be responsible for implementing and maintaining their respective management systems while collaborating with other teams to ensure integration and alignment.
- Identify Common Processes: Identify processes that are common across different management systems. This involves mapping out the various processes, such as document control, training, internal audits, corrective actions, and management reviews, and identifying areas of overlap or potential synergies.
- Implement Integrated Processes: Develop and implement integrated processes that encompass the requirements of all management systems involved. This includes updating or developing procedures, work instructions, and documentation to reflect the integrated approach. Ensure that roles, responsibilities, and communication channels are clearly defined.
- Training and Awareness: Provide training and awareness programs to employees regarding the integrated management system and its benefits. This helps employees understand their roles and responsibilities, encourages active participation, and fosters a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement.
- Performance Monitoring and Measurement: Establish a system for monitoring and measuring the performanece of the integrated management system. This includes setting performance indicators, conducting regular audits, collecting data, and analyzing results to assess the effectiveness of the system and identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: Promote a culture of continuous improvement within the organization. Encourage employees to provide feedback, suggestions, and innovative ideas to enhance the integrated management system. Regularly review the system’s performance, conduct management reviews, and implement corrective actions to drive continual improvement.
- Certification and Compliance: If desired, organizations can seek certification for the integrated management system. Engage with a recognized certification body to undergo an audit and achieve certification, demonstrating compliance with the relevant management system standards and the successful integration of the systems.
Implementing an EMS with IMS2 methodology allows organizations to streamline their management systems, optimize resources, improve efficiency, and enhance overall performance. By integrating processes, aligning objectives, and fostering collaboration, organizations can achieve a more holistic and sustainable approach to managing their environmental responsibilities while benefiting from the advantages of an integrated management system.
Why should you implement ISO 14001 in your organization?
Implementing ISO 14001, the Environmental Management System (EMS) standard, in your organization can bring numerous benefits and advantages. Here are some compelling reasons why you should consider implementing ISO 14001:
- Legal Compliance: ISO 14001 helps organizations ensure compliance with environmental laws, regulations, and other requirements. By implementing the standard, you can identify and understand the relevant legal obligations that apply to your organization’s environmental aspects. This helps you avoid non-compliance penalties, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
- Improved Environmental Performance: ISO 14001 provides a framework for systematically managing and improving your organization’s environmental performance. It helps identify significant environmental aspects, set objectives and targets, and implement measures to minimize environmental impact. By focusing on continual improvement, ISO 14001 enables you to enhance your environmental performance and reduce resource consumption, waste generation, and pollution.

- Enhanced Efficiency and Cost Savings: Implementing ISO 14001 encourages organizations to assess their processes, identify inefficiencies, and implement measures to improve resource management. By optimizing resource utilization, reducing waste, and improving energy efficiency, you can achieve cost savings in areas such as energy consumption, waste disposal, and raw material usage.
- Competitive Advantage: ISO 14001 certification is globally recognized and demonstrates your organization’s commitment to environmental responsibility. It can enhance your reputation, increase stakeholder trust, and provide a competitive edge in the marketplace. Many customers and business partners prefer to work with environmentally responsible organizations, giving you a competitive advantage over non-certified competitors.
- Risk Management: ISO 14001 emphasizes a risk-based approach to environmental management. By identifying and assessing environmental risks and their potential impacts, you can implement controls and mitigation measures to prevent or minimize adverse events. This helps safeguard your organization against environmental incidents, reputational damage, and financial liabilities.
- Stakeholder Engagement: ISO 14001 promotes stakeholder engagement and encourages organizations to communicate their environmental performance and initiatives to relevant stakeholders. This fosters transparency, builds trust, and improves relationships with customers, suppliers, employees, regulatory bodies, and local communities.
- Regulatory and Supply Chain Requirements: ISO 14001 certification can help meet regulatory requirements and demonstrate compliance to government authorities. Additionally, many organizations, particularly in the supply chain, require their suppliers to have ISO 14001 certification. Implementing ISO 14001 can ensure you meet these requirements and maintain strong business relationships.
- Employee Engagement and Morale: ISO 14001 implementation provides a framework for engaging employees in environmental management. Involving employees in setting objectives, conducting audits, and suggesting improvements fosters a sense of ownership, boosts morale, and enhances job satisfaction. Employees who feel engaged and valued are more likely to contribute to the organization’s environmental goals.
- Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility: Implementing ISO 14001 aligns your organization with the principles of sustainability and corporate social responsibility. It demonstrates your commitment to minimizing environmental impact, conserving resources, and contributing to a sustainable future. This can positively influence your brand image and attract socially conscious customers, investors, and partners.
- Continuous Improvement Culture: ISO 14001 promotes a culture of continual improvement by requiring organizations to set objectives, measure performance, conduct audits, and take corrective actions. This culture of ongoing improvement can extend beyond environmental management to other areas of your organization, fostering a proactive and adaptive mindset.
Overall, implementing ISO 14001 offers significant benefits, including legal compliance, improved environmental performance, cost savings, competitive advantage, and stakeholder engagement. It demonstrates your organization’s commitment to sustainability and provides a framework for continual improvement, positioning you as a responsible and forward-thinking organization in today’s environmentally conscious world.
Conclusion:
ISO 14001 Certification in Nepal represents a pivotal step for organizations looking to solidify their commitment to environmental responsibility. As Nepal continues to develop economically, the challenge of balancing growth with sustainability becomes increasingly paramount. By adopting ISO 14001, organizations in Nepal can not only align themselves with global best practices but also showcase their dedication to minimizing their environmental footprint. Furthermore, the certification provides a structured framework that assists organizations in meeting local environmental regulations, optimizing resource use, and opening new avenues for international trade and recognition. As Nepal grapples with environmental challenges, from waste management to conservation efforts, ISO 14001 emerges as a beacon of proactive environmental management and stewardship.
Frequently Asked Question:
What is Environment Management System (EMS)?
How are Nepal’s environment managed?
How can local governance of Nepal introduce environment management issues?
Local governance in Nepal can introduce environment management issues by implementing effective environmental policies, promoting sustainable practices, and encouraging community involvement. By raising awareness about environmental challenges and fostering responsible environmental practices, local governments can play a crucial role in addressing issues such as waste management, pollution control, conservation of natural resources, and sustainable development at the grassroots level.
What is ISO 14001 Certification?
ISO 14001 Certification is an internationally recognized standard that outlines the requirements for an Environmental Management System (EMS). It helps organizations establish, implement, maintain, and improve their environmental performance, ensuring they comply with environmental regulations and reduce their environmental impact.
Why should my organization get ISO 14001 Certified?
Obtaining ISO 14001 Certification showcases your commitment to environmental responsibility, sustainability, and efficient resource management. It enhances your organization’s reputation, opens up new business opportunities, and demonstrates compliance with environmental regulations, gaining the trust of stakeholders and customers.
Is ISO 14001 Certification mandatory in Nepal?
ISO 14001 Certification is not mandatory in Nepal. However, many organizations voluntarily seek certification to improve their environmental practices and demonstrate their dedication to sustainability.
How long does it take to get ISO 14001 Certified?
The time to obtain ISO 14001 Certification can vary based on the size and complexity of your organization. Typically, the process takes several months, involving gap analysis, implementation of EMS, internal audits, and the final certification audit.
Can small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) get ISO 14001 Certified?
Yes, ISO 14001 Certification is suitable for organizations of all sizes, including SMEs. The standard is scalable and adaptable to fit the specific needs and scope of any business.
How much does ISO 14001 Certification cost in Nepal?
The cost of ISO 14001 Certification depends on factors such as the size of your organization, the complexity of your processes, and the certification body you choose. It is best to request quotes from different certification providers to get an accurate estimate.
Who can certify my organization for ISO 14001 in Nepal?
Only accredited certification bodies can issue ISO 14001 Certifications. Ensure that you choose a reputable and accredited certification body that is recognized by international accreditation bodies.
What is the validity period of ISO 14001 Certification?
ISO 14001 Certification is valid for three years. During this period, your organization will need to undergo annual surveillance audits to ensure continued compliance with the standard’s requirements.
Can I integrate ISO 14001 with other management system standards?
Yes, ISO 14001 is designed to be compatible with other management system standards, such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety). This integration allows for streamlined processes and a more efficient management system.
How can Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd. assist my organization in obtaining ISO 14001 Certification?
Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd. is a trusted certification body with experienced auditors and experts in environmental management systems. We will guide your organization through the certification process, provide valuable insights, conduct audits, and ensure your successful achievement of ISO 14001 Certification.
In order to maintain a seamless and efficient ISO certification process, partnering with a trusted ISO consultant is crucial. At Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd., we are committed to providing your organization with expert guidance and support, ensuring a cost-effective and successful ISO implementation journey. As the leading ISO System Certification body in Nepal, we offer a comprehensive range of certification services tailored to your organization’s needs.
Our dedicated team is ready to provide your organization with customized solutions and expert assistance. If you have any queries or are ready to embark on your ISO certification journey, feel free to contact us at 9840525565 for a free consultation on our ISO certification services. Trust Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd. to be your partner in achieving excellence and compliance.