ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Information Security, Cybersecurity and Privacy Protection.
In today’s digital age, where data breaches and cyber-attacks are becoming increasingly prevalent, safeguarding sensitive information is paramount for any organization. ISO 27001:2022, the latest version of the internationally recognized standard for Information Security Management System (ISMS), provides a robust framework to protect your organization’s valuable data from potential threats. In this article, we will delve into the meaning of ISO 27001, explore its framework, and highlight the three core principles that underpin its information security management system.

What does ISO 27001 mean?
ISO 27001 is a globally accepted standard developed and maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). It defines the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System within an organization.
This standard sets out a risk-based approach, focusing on identifying and mitigating potential information security risks. By adhering to ISO 27001, organizations can ensure that their information assets are protected from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, and destruction. The standard covers not only digital information but also physical and environmental security, making it comprehensive and adaptable to various industries and sectors.
ISO framework and the purpose of ISO 27001:
The ISO 27001 framework provides a systematic approach to managing an organization’s information security risks. It comprises the following key components:
A. Risk Assessment: ISO 27001 emphasizes the importance of conducting a thorough risk assessment to identify potential security threats and vulnerabilities. This involves understanding the organization’s assets, their value, and the possible impact of security breaches. By understanding the risks, organizations can prioritize their security efforts and allocate resources effectively.
B. Risk Treatment: Once the risks are identified, the organization needs to implement appropriate controls to treat or mitigate these risks. These controls can include technical measures, policies, procedures, and employee awareness programs. The aim is to reduce the risk exposure to an acceptable level and prevent or minimize potential security incidents.
C. Continuous Improvement: ISO 27001 advocates for a continuous improvement process. Regular reviews and evaluations help organizations adapt to new threats and changes in their operating environment. This iterative approach ensures that the information security management system remains effective and aligned with the organization’s evolving needs.
The primary purpose of ISO 27001 is to instill confidence in stakeholders, including customers, partners, and regulatory authorities, that an organization takes information security seriously and has implemented appropriate measures to protect their data. Certification to ISO 27001 demonstrates a commitment to best practices in information security and can give organizations a competitive edge in the marketplace.
What are the three principles of ISO 27001 Information Security Management System?
- Confidentiality:This principle focuses on ensuring that access to sensitive information is restricted to authorized individuals only. By implementing access controls, encryption, and secure data handling procedures, organizations can maintain confidentiality and prevent unauthorized disclosure.
- Integrity:The principle of integrity ensures that information remains accurate, reliable, and unaltered. Measures such as data validation, version control, and audit trails help maintain the integrity of information, reducing the risk of data tampering or manipulation.
- Availability: This principle emphasizes the importance of making information accessible to authorized users when they need it. By implementing redundancy, disaster recovery plans, and robust IT infrastructure, organizations can ensure the availability of critical systems and data, even in the face of unexpected event.
ISO/IEC 27001, the standard for Information Security Management System (ISMS), is of utmost importance in today’s digital landscape due to several compelling reasons.
Why is an information security management ISO/IEC 27001 important?
- Protection of Information Assets: Information is one of the most valuable assets for any organization. ISO/IEC 27001 provides a systematic and structured approach to safeguarding sensitive information, including customer data, financial records, intellectual property, and trade secrets. By implementing the standard’s requirements, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction of critical information.
- Mitigating Security Risks: Cybersecurity threats and data breaches have become prevalent, and their consequences can be severe, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage. ISO/IEC 27001’s risk-based approach ensures that organizations identify and assess potential security risks, enabling them to implement appropriate controls to mitigate these risks effectively.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with various data protection laws and industry regulations is a legal obligation for organizations worldwide. ISO/IEC 27001 helps organizations align their information security practices with relevant legal and regulatory requirements. Meeting these standards can mitigate legal liabilities and potential fines associated with data breaches and non-compliance.
- Business Continuity and Resilience: Information security incidents can disrupt operations, leading to downtime, loss of revenue, and decreased productivity. By establishing an ISMS based on ISO/IEC 27001, organizations can enhance their resilience to cyber-attacks, minimize downtime, and ensure business continuity in the face of security incidents.
- Customer Trust and Confidence: In today’s highly competitive business landscape, customers place a significant emphasis on data privacy and security. ISO/IEC 27001 certification demonstrates an organization’s commitment to protecting customer data and sensitive information. This builds trust and confidence among customers, stakeholders, and partners, leading to a competitive advantage and enhanced brand reputation.
- Supply Chain Assurance: Organizations are increasingly interconnected through complex supply chains. Suppliers and partners may handle sensitive information on behalf of their clients. ISO/IEC 27001 certification provides assurance that these entities have implemented robust information security practices, reducing the overall risk to the supply chain.
- Improved Management and Processes: Implementing ISO/IEC 27001 involves defining roles, responsibilities, and processes related to information security. This fosters better communication, collaboration, and coordination among employees, resulting in improved management practices and greater efficiency in handling security incidents.
- Cost Savings: Proactively addressing information security through ISO/IEC 27001 can lead to cost savings in the long run. By preventing security incidents, organizations can avoid the financial burden associated with recovering from data breaches, legal penalties, and reputational damage.
- Global Recognition: ISO/IEC 27001 is an internationally recognized standard. Achieving certification demonstrates an organization’s commitment to adhering to best practices in information security on a global scale. This recognition can open doors to new markets and potential business opportunities.
Why Should a Company Adopt ISO 27001? Is ISO 27001 Certification Worth It?
Adopting ISO 27001 and pursuing ISO 27001 certification can bring several benefits to a company. Here are some reasons why a company should consider adopting ISO 27001:
- Comprehensive Information Security Management: ISO 27001 provides a holistic and systematic approach to managing information security within an organization. It covers various aspects such as risk assessment, control implementation, incident response, and continual improvement. By adopting ISO 27001, a company can establish a structured framework to protect its sensitive information assets effectively.
- Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements: ISO 27001 helps companies meet legal and regulatory obligations related to information security. By aligning their practices with ISO 27001 requirements, organizations can ensure they have implemented appropriate controls and measures to comply with relevant laws and regulations. This can prevent legal penalties, fines, and reputational damage resulting from non-compliance.
- Enhanced Reputation and Trust: ISO 27001 certification demonstrates a company’s commitment to best practices in information security. It provides an independent validation of the company’s adherence to international standards. By earning ISO 27001 certification, a company can build trust and confidence among its customers, partners, and stakeholders, showing that it takes data protection seriously.
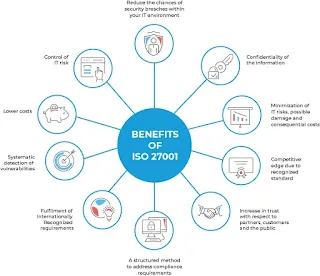
- Competitive Advantage: ISO 27001 certification can provide a competitive edge in the marketplace. In industries where information security is a critical concern, certification can differentiate a company from its competitors. Potential clients and partners may prioritize working with certified organizations, as ISO 27001 provides assurance of the company’s ability to protect sensitive information and maintain a robust security posture.
- Risk Management: ISO 27001’s risk-based approach helps companies identify and mitigate potential security risks. By conducting risk assessments and implementing appropriate controls, organizations can reduce the likelihood and impact of security incidents. This proactive approach to risk management can minimize financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruptions caused by data breaches or cyber-attacks.
- Continual Improvement: ISO 27001 promotes a culture of continual improvement in information security management. It encourages organizations to regularly review and enhance their security controls, processes, and policies. By continuously assessing and adapting to emerging threats and technologies, companies can stay ahead of potential risks and maintain an effective security posture.
However, it’s important to consider the specific needs and circumstances of each company when evaluating the worth of ISO 27001 certification. The certification process can require investment in terms of time, resources, and costs associated with audits and assessments. Companies should weigh these factors against the potential benefits and their business objectives to determine if ISO 27001 certification aligns with their strategic goals.
Ultimately, for companies that handle sensitive information and prioritize information security, ISO 27001 certification can be a valuable investment that enhances their reputation, strengthens their security practices, and provides a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
How does ISO 27001 work?
ISO 27001 works by providing a systematic framework for implementing and managing an Information Security Management System (ISMS) within an organization. Here is an overview of how ISO 27001 works:
-
- Establishing the Context: The organization determines the scope of the ISMS and identifies the internal and external factors that may impact its information security objectives. This involves understanding the organization’s context, including its business environment, legal requirements, and stakeholder expectations.
- Leadership and Management Commitment: Top management plays a crucial role in driving the implementation of ISO 27001. They establish the information security policy, define roles and responsibilities, allocate necessary resources, and demonstrate their commitment to information security.
- Risk Assessment: ISO 27001 adopts a risk-based approach to information security management. The organization conducts a systematic risk assessment process to identify and evaluate potential risks to its information assets. This involves identifying assets, assessing their vulnerabilities and threats, and determining the potential impact of security incidents.
- Risk Treatment and Control Implementation: Based on the risk assessment, the organization selects appropriate risk treatment options to mitigate or manage the identified risks. Controls are implemented to address the identified vulnerabilities and threats. These controls can be technical, operational, or managerial in nature and aim to reduce the risks to an acceptable level.

- Documentation and Implementation: The organization develops and implements policies, procedures, and guidelines to support the ISMS. This includes documenting the information security policy, defining operational procedures, and establishing guidelines for various security controls and practices. Training and awareness programs are conducted to ensure employees understand their roles and responsibilities in information security.
- Monitoring and Measurement: ISO 27001 emphasizes the importance of ongoing monitoring and measurement of the ISMS. The organization establishes processes for monitoring the effectiveness of controls, conducting internal audits, and performing regular management reviews. This enables the organization to identify non-conformities, areas for improvement, and ensure the ISMS remains effective and aligned with business objectives.
- Continual Improvement: ISO 27001 promotes a culture of continual improvement in information security management. The organization analyzes the results of audits, reviews, and assessments to identify opportunities for improvement. Corrective and preventive actions are taken to address identified issues and enhance the ISMS. Regular updates and revisions are made to policies, procedures, and controls to adapt to changes in the internal and external environment.
- Certification: While certification to ISO 27001 is not mandatory, organizations can choose to undergo an independent audit by a recognized certification body. The certification process involves assessing the organization’s ISMS against the requirements of ISO 27001. Upon successful completion, the organization receives ISO 27001 certification, which demonstrates its conformity to international standards for information security
Learn more about the key features of ISO 27001
ISO 27001, as an international standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS), encompasses several key features that contribute to its effectiveness and relevance. Here are the key features of ISO 27001:
- Risk-based Approach: ISO 27001 adopts a risk-based approach to information security management. It emphasizes the identification, assessment, and management of information security risks within an organization. This approach ensures that security controls and measures are implemented in a targeted and prioritized manner, focusing on the most significant risks.
- PDCA Cycle: ISO 27001 follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, a continuous improvement model widely used in quality management systems. This cycle provides a structured framework for organizations to plan, implement, monitor, and improve their information security practices. The PDCA cycle enables organizations to establish, maintain, and enhance their ISMS effectively.
- Comprehensive Coverage: ISO 27001 provides a comprehensive framework for managing information security. It covers various aspects, including risk assessment, security policy, asset management, human resources security, physical and environmental security, communication and operations management, access control, cryptography, incident management, business continuity, and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: ISO 27001 is designed to be flexible and adaptable to different organizations and industries. It provides a set of requirements that can be tailored to the specific needs and context of an organization. This flexibility allows organizations to implement controls and practices that are appropriate and relevant to their unique information security risks and business requirements.
- Integration with Business Processes: ISO 27001 encourages the integration of information security management into the overall business processes of an organization. It emphasizes the need to align information security objectives and controls with the organization’s strategic goals and operational activities. This integration ensures that information security becomes an integral part of the organization’s culture and operations.
- Continual Improvement: ISO 27001 promotes a culture of continual improvement in information security management. It requires organizations to regularly review and evaluate the effectiveness of their ISMS and take corrective and preventive actions as necessary. This continual improvement approach helps organizations stay proactive in identifying and addressing emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Documentation and Evidence-based Approach: ISO 27001 places importance on the documentation of policies, procedures, guidelines, and records related to information security. It requires organizations to maintain documented evidence of their information security activities and controls. This documentation helps ensure consistency, traceability, and accountability in information security management practices.

- Compliance and Certification: ISO 27001 provides a recognized benchmark for information security management. While certification to ISO 27001 is not mandatory, organizations can choose to undergo a certification audit by an accredited certification body. Certification demonstrates the organization’s conformity to the requirements of ISO 27001 and provides assurance to stakeholders regarding its commitment to information security.
These key features make ISO 27001 a robust and flexible standard for organizations seeking to establish and maintain effective information security management systems. By implementing ISO 27001, organizations can enhance their ability to protect sensitive information, manage risks, comply with legal and regulatory requirements, and build trust with stakeholders
How Much Does the ISO 27001 Certification Cost?
The cost of ISO 27001 certification can vary depending on several factors, including the size and complexity of the organization, the scope of the certification, the chosen certification body, and the level of readiness of the organization’s existing information security management system. Here are some cost factors to consider:
- Gap Analysis and Readiness Assessment: Before pursuing ISO 27001 certification, many organizations opt to conduct a gap analysis or readiness assessment to identify any gaps or areas for improvement in their existing information security practices. The cost of these assessments can vary based on the depth and scope of the assessment and the expertise of the consultants or auditors involved.
- Training and Education: ISO 27001 certification often requires employees to be trained on information security management principles, the requirements of the standard, and the implementation of controls. Training costs can vary depending on the number of employees to be trained and the training provider chosen.
- Documentation Development: ISO 27001 certification necessitates the development and documentation of policies, procedures, and other required documentation for the Information Security Management System (ISMS). The cost will depend on the complexity and extent of the documentation required and whether organizations choose to develop the documentation internally or engage external consultants.
- Internal Resources and Implementation: Implementing ISO 27001 may require dedicated internal resources, including personnel responsible for managing the ISMS, conducting risk assessments, implementing controls, and monitoring compliance. The cost will depend on the time and effort allocated to these activities and the organization’s structure and resources.
- External Audit and Certification: The primary cost associated with ISO 27001 certification is the audit and certification process itself. This includes the costs charged by the certification body for conducting the initial certification audit, as well as any surveillance audits required for ongoing certification maintenance. Certification costs can vary based on the size and complexity of the organization and the chosen certification body’s fees.
It’s important to note that there is no standardized pricing for ISO 27001 certification as it depends on the factors mentioned above. It is recommended for organizations to obtain quotes from multiple certification bodies, compare their services, reputation, and pricing, and consider the overall value provided before making a decision
Why Choose us for ISO 27001?
When it comes to choosing a specific organization for ISO 27001 certification, it’s essential to highlight your unique qualities and value propositions. While I don’t have specific information about your organization, here are some potential reasons why clients might choose you for ISO 27001:
- Expertise and Experience: Emphasize your organization’s expertise and experience in implementing and certifying ISO 27001. Highlight the qualifications, certifications, and experience of your team members who are responsible for guiding clients through the certification process. Showcase successful case studies or testimonials from satisfied clients.
- Industry Knowledge: If you have specialized knowledge or experience in a specific industry, highlight how that expertise can benefit clients within that industry. Understanding the unique challenges and requirements of different sectors can help tailor the ISO 27001 implementation to their specific needs.
- Client-Centric Approach: Focus on your commitment to providing exceptional customer service and a client-centric approach. Emphasize your ability to listen to clients, understand their goals and challenges, and customize your services to meet their specific requirements. Showcase your responsiveness, clear communication channels, and willingness to go the extra mile for client satisfaction.
- Comprehensive Services: Highlight the range of services you offer beyond just ISO 27001 certification. This may include pre-assessment gap analysis, training programs, ongoing support, and assistance with implementing and maintaining the Information Security Management System (ISMS). Emphasize that you provide end-to-end solutions to ensure a smooth and successful certification process.
- Reputation and Credibility: Showcase your organization’s reputation and credibility in the field of information security and ISO 27001 certification. Highlight any industry awards, accreditations, or partnerships that validate your expertise and commitment to delivering high-quality services. Share success stories and client testimonials that demonstrate your track record of delivering value.
- Cost-Effectiveness: If your pricing is competitive or offers added value for the cost, emphasize that aspect. Explain how your pricing structure provides a cost-effective solution without compromising the quality and integrity of the certification process. Showcase the return on investment clients can expect from partnering with you.
- Continuous Improvement: Communicate your commitment to continuous improvement in information security practices. Highlight your organization’s efforts to stay up-to-date with the latest industry trends, emerging threats, and regulatory requirements. Demonstrate how you assist clients in evolving their information security management systems over time to maintain effectiveness.
What are the ISO 27001 controls?
ISO 27001 specifies a set of controls that organizations can implement to address various information security risks and requirements. These controls are grouped into 14 sections, each addressing specific aspects of information security management. The controls are commonly referred to as Annex A controls. Here are the main sections and a brief overview of some of the ISO 27001 controls within each section:
Information Security Policies :
- Information Security Policies and Procedures: Develop and implement an information security policy and supporting procedures to guide information security activities within the organization.
Organization of Information Security :
- Internal Organization: Define roles and responsibilities for information security and ensure clear accountability.
- Mobile Devices and Teleworking: Securely manage mobile devices and teleworking practices to protect information.
Human Resource Security :
- Prior to Employment: Implement security measures during the hiring process to ensure information security.
- During Employment: Educate employees about information security and their responsibilities.
- Termination or Change of Employment: Establish procedures for handling the departure or change of employment of employees to prevent unauthorized access to information.
Asset Management :
- Responsibility for Assets: Assign ownership and responsibility for information assets.
- Information Classification: Classify information according to its value and sensitivity to ensure appropriate protection.
Access Control :
- Access Control Policy: Establish access control policies to control access to information resources.
- User Access Management: Implement procedures for granting, modifying, and revoking user access to information systems.
- User Responsibilities: Define user responsibilities for information security.
Cryptography :
- Cryptographic Controls: Implement cryptographic controls to protect sensitive information.
Physical and Environmental Security :
- Secure Areas: Secure physical areas where information is processed, stored, or transmitted.
- Equipment Security: Protect information processing equipment and assets.
- Clear Desk and Clear Screen Policy: Implement policies to secure workstations and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Operations Security :
- Operational Procedures and Responsibilities: Establish and maintain operational procedures and responsibilities for secure information processing.
- Protection from Malware: Protect information systems from malware threats.
Communications Security :
- Network Security Management: Manage network security to protect information during transmission.
- Information Transfer: Implement security measures to protect information during transfer.
System Acquisition, Development, and Maintenance :
- Security Requirements of Information Systems: Define and implement security requirements for information systems.
- Security in Development and Support Processes: Integrate security into the system development and support processes.
Supplier Relationships :
- Information Security in Supplier Relationships: Ensure information security requirements are met when working with external suppliers.
Information Security Incident Management :
- Responsibilities and Procedures: Establish procedures for reporting, managing, and resolving information security incidents.
Information Security Aspects of Business Continuity Management :
- Information Security Continuity: Establish and maintain plans to ensure the continuity of information security during adverse events.
Compliance :
- Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements: Identify and comply with relevant laws, regulations, and contractual requirements.
Each control provides specific requirements or guidelines to help organizations address the corresponding information security risks. Organizations can select and implement controls based on their specific needs, risk assessments, and legal/regulatory obligations.
It’s important to note that the specific controls applicable to an organization may vary based on factors such as the organization’s size, industry, and specific risk profile. Organizations should conduct a thorough risk assessment to determine the most relevant controls to implement within their Information Security Management System (ISMS).
How many controls are there in ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 includes a total of 114 controls that are specified in Annex A of the standard. These controls are organized into 14 sections, each addressing a specific aspect of information security management. The controls in Annex A provide a comprehensive framework for organizations to establish and maintain an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS) to protect their information assets. It’s worth noting that not all controls will be applicable to every organization, as their relevance depends on the organization’s specific risks, requirements, and the scope of the ISMS implementation. Organizations should conduct a risk assessment to identify the controls that are most relevant to their information security needs
Requirements: Two parts of the standard
The ISO 27001 standard consists of several requirements that organizations must fulfill to establish and maintain an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS). These requirements are outlined in two main parts of the standard:
Part 1: The Management System Requirements (Clauses 4-10):
-
- Context of the Organization: The organization must determine the internal and external factors relevant to its information security management system and define the scope of the ISMS.
- Leadership: Top management must demonstrate leadership and commitment to the ISMS, establish an information security policy, and define roles and responsibilities.
- Planning: The organization must conduct a risk assessment and establish risk treatment processes to identify and address information security risks and opportunities.
- Support: Provide the necessary resources, competence, awareness, communication, and documented information to support the ISMS.
- Operation: Implement and manage the ISMS controls to address identified risks and ensure the effective implementation of the information security policy and objectives.
- Performance Evaluation: Establish processes to monitor, measure, analyze, and evaluate the performance of the ISMS, including internal audits and management reviews.
- Improvement: Continually improve the suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness of the ISMS through corrective actions, preventive actions, and management of nonconformities.
Part 2: The Annex A Controls:
-
- Annex A of ISO 27001 contains a set of 114 controls that are categorized into 14 sections, addressing specific aspects of information security management. These controls cover areas such as information security policies, asset management, access control, cryptography, physical and environmental security, incident management, business continuity, and more. Organizations are required to select and implement the controls that are applicable to their specific context and information security risks.
These two parts work together to provide a comprehensive framework for organizations to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve their ISMS, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information assets. Compliance with both the management system requirements and the Annex A controls is necessary to achieve ISO 27001 certification.
How to achieve ISO 27001 compliance?
Achieving ISO 27001 compliance involves a systematic approach and several key steps. Here is a general outline of the process:
- Understand the Standard: Familiarize yourself with the ISO 27001 standard and its requirements. Read and study the standard thoroughly to gain a comprehensive understanding of the compliance criteria.
- Establish the Context: Determine the scope of your Information Security Management System (ISMS) and identify the internal and external factors that may impact your information security objectives.
- Conduct a Risk Assessment: Perform a comprehensive risk assessment to identify and assess potential information security risks and vulnerabilities within your organization. This includes evaluating the likelihood and impact of risks on your information assets.
- Develop an Information Security Management System: Establish an ISMS based on the requirements of ISO 27001. This includes defining policies, procedures, and controls to address identified risks and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets.
- Implement Controls: Select and implement the controls specified in Annex A of ISO 27001 that are relevant to your organization’s context and risks. This involves putting in place measures to address areas such as access control, physical security, incident management, etc.
- Train and Raise Awareness: Educate your employees about the importance of information security, their roles and responsibilities, and the policies and procedures in place. Raise awareness to foster a culture of information security within your organization.
- Perform Internal Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to assess the effectiveness and compliance of your ISMS. This helps identify areas for improvement and ensures that your organization remains on track towards ISO 27001 compliance.
- Corrective Actions: Address any non-conformities or gaps identified during internal audits through corrective actions. This involves taking appropriate measures to rectify deficiencies and improve your ISMS.
- Management Review: Conduct periodic management reviews to evaluate the performance and effectiveness of your ISMS. Use these reviews to assess the continued suitability and relevance of your information security policies, objectives, and controls.
- External Certification Audit: Engage an accredited certification body to perform an independent assessment of your ISMS against the requirements of ISO 27001. The certification body will conduct an audit to determine if your organization meets the compliance criteria.
- Maintain and Continually Improve: ISO 27001 compliance is an ongoing process. Continually monitor, review, and update your ISMS to address emerging risks, changing business needs, and evolving security threats. Stay abreast of changes in the standard and industry best practices to ensure ongoing compliance.
It’s important to note that achieving ISO 27001 compliance requires commitment, resources, and a culture of information security throughout the organization. It is recommended to seek guidance from experienced professionals or consultants who specialize in ISO 27001 implementation to ensure a smooth and successful compliance journey.

Clause 5: Leadership
Clause 5 of ISO 27001 focuses on the role of leadership in establishing and maintaining an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS). Let’s dive into each subclause:
Leadership and commitment: This subclause emphasizes the crucial role of top management in leading the organization’s information security efforts. Top management must demonstrate a clear commitment to information security and actively support the implementation of the ISMS. This commitment includes providing the necessary resources, establishing information security objectives, and promoting a culture of security throughout the organization.
Policy: In this subclause, organizations are required to establish an information security policy. The policy should outline the organization’s commitment to protecting its information assets and the overall goals of the ISMS. The policy should be documented, communicated, and understood by all employees. It provides a framework for setting information security objectives and serves as a reference point for making decisions related to information security.
Organizational roles, responsibilities, and authorities: This subclause focuses on defining and communicating the roles, responsibilities, and authorities related to information security within the organization. It is essential to clearly assign responsibilities for implementing and maintaining various aspects of the ISMS, such as risk management, incident response, and security awareness. By doing so, the organization ensures that everyone understands their roles in protecting information assets and managing information security effectively.
To comply with Clause 5, organizations need to ensure that top management actively participates in the information security process and is committed to its success. This involves creating a robust information security policy and ensuring that roles and responsibilities are clearly defined and communicated. By providing strong leadership, organizations can instill a security-conscious culture and drive the successful implementation of the ISMS, resulting in effective protection of information assets and improved resilience against security threats.
Clause 6: Planning
Clause 6 of ISO 27001 focuses on the planning aspects of an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It provides guidance on how organizations should identify, assess, and address risks and opportunities related to information security, as well as establish objectives, plans, and controls to achieve a secure and compliant environment. Let’s explore each subclause:
Actions to address risks and opportunities: This subclause emphasizes the importance of taking proactive actions to address information security risks and opportunities. Organizations are required to establish a systematic approach to identify and assess risks and opportunities, and to determine appropriate actions to address them. This includes implementing preventive measures, establishing controls, and continuously monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of these actions.
Information security objectives and plans to achieve them: Organizations need to establish information security objectives that are consistent with the overall business objectives and the context of the organization. Objectives should be measurable, achievable, and aligned with applicable legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements. Plans should be developed to achieve these objectives, including the identification of necessary resources, responsibilities, and timelines.
Information security risk assessment: This subclause focuses on conducting an information security risk assessment. Organizations need to identify and assess the risks to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets. This includes considering internal and external threats, vulnerabilities, and the potential impact of incidents. The risk assessment helps prioritize actions and allocate resources effectively.
Information security risk treatment: Once risks are identified and assessed, organizations must determine and implement appropriate risk treatment measures. This involves selecting and applying information security controls to mitigate or eliminate identified risks. Risk treatment should consider the effectiveness, feasibility, and cost of controls, as well as legal and regulatory requirements.
Information security controls: Organizations need to select and implement information security controls based on the identified risks and treatment decisions. ISO 27001 provides a comprehensive set of controls in Annex A, categorized into various domains such as access control, asset management, cryptography, and incident management. Organizations should tailor the selection and implementation of controls to their specific context and risks.
Planning the management of incidents: Organizations should establish plans and procedures to manage information security incidents effectively. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, establishing incident response procedures, and conducting regular exercises and tests to ensure preparedness. The objective is to minimize the impact of incidents, restore normal operations, and learn from the experience to prevent future occurrences.
Business continuity management: Organizations need to develop and implement business continuity management plans to ensure the continuity of critical business functions during and after disruptive events. This includes identifying critical processes, conducting business impact analyses, developing response and recovery plans, and testing and reviewing the effectiveness of these plans.
Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements: Organizations must establish processes to ensure compliance with applicable legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements related to information security. This includes identifying and understanding relevant requirements, implementing controls to address these requirements, and regularly monitoring and reviewing compliance.
By addressing the requirements of Clause 6, organizations can effectively plan and establish the necessary frameworks, objectives, and controls to manage information security risks and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information assets.
Clause 7: Support
Clause 7 of ISO 27001 focuses on the support required for an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS). It highlights the importance of providing the necessary resources, competence, awareness, and communication to ensure the successful implementation and maintenance of the ISMS. Let’s explore each subclause:
Resources: This subclause emphasizes the need for organizations to allocate the necessary resources to support the ISMS. Resources can include financial, human, technological, and infrastructure resources. Organizations must ensure that these resources are adequate and appropriate for the implementation, operation, monitoring, and improvement of the ISMS.
Competence: Competence refers to the knowledge, skills, and expertise required by individuals involved in the ISMS. This subclause highlights the importance of determining the necessary competence levels for different roles within the organization. Organizations should identify competency requirements, provide training and education to enhance skills, and evaluate the effectiveness of competence development initiatives.
Awareness: Creating awareness about information security among employees is crucial for the successful implementation of the ISMS. This subclause emphasizes the need for organizations to ensure that all employees understand the importance of information security, their roles and responsibilities, and the potential consequences of non-compliance. Awareness programs, training, and communication initiatives should be implemented to promote a culture of security throughout the organization.
Communication: Effective communication plays a vital role in ensuring the success of the ISMS. This subclause highlights the importance of establishing communication channels and processes to facilitate the flow of information related to information security. Communication should occur both internally, among employees and stakeholders, and externally, with relevant parties such as customers, suppliers, and regulatory authorities. Communication helps in sharing information, addressing concerns, and ensuring a coordinated approach to information security.
By addressing the requirements of Clause 7, organizations can provide the necessary support for the implementation and maintenance of the ISMS. This includes allocating resources, developing competence, raising awareness, and establishing effective communication channels. These elements contribute to the effectiveness and efficiency of the ISMS, ensuring that information security is managed comprehensively and consistently throughout the organization.
Clause 8:Operation
Clause 8 of ISO 27001 focuses on the operational aspects of an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It covers key areas such as planning and control, risk management, incident management, and monitoring and evaluation. Let’s explore each subclause:
Operational planning and control: This subclause emphasizes the need for organizations to establish processes for operational planning and control related to information security. It involves identifying and implementing controls to mitigate information security risks, ensuring the appropriate allocation of resources, establishing operational procedures, and monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of these controls.
Information security risk management: Effective risk management is essential for maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets. This subclause focuses on identifying, assessing, and treating information security risks. Organizations need to establish a systematic approach to risk management, including the identification of assets, threat assessment, vulnerability analysis, and the selection and implementation of appropriate risk treatment measures.
Information security incident management: Incident management is crucial for responding to and managing information security incidents effectively. This subclause requires organizations to establish an incident management process, including incident identification, reporting, assessment, response, and recovery. It also emphasizes the need for organizations to learn from incidents and take corrective actions to prevent their recurrence.
Monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation: To ensure the effectiveness of the ISMS, organizations must establish processes for monitoring, measuring, analyzing, and evaluating their information security performance. This subclause includes requirements for monitoring the implementation of information security controls, conducting internal audits, analyzing security incidents and trends, and evaluating the overall performance of the ISMS. The results of these activities can provide insights for continual improvement.
By addressing the requirements of Clause 8, organizations can establish effective operational planning and control mechanisms, manage information security risks, handle incidents efficiently, and monitor and evaluate the performance of the ISMS. These activities contribute to maintaining a robust and resilient information security posture, enabling organizations to protect their valuable information assets and meet their information security objectives.
Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
Clause 9 of ISO 27001 focuses on the evaluation and improvement of an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It includes requirements for conducting internal audits and management reviews to assess the effectiveness of the ISMS and identify areas for improvement. Let’s explore each subclause:
Internal audit: Internal audits are systematic and independent evaluations of the ISMS to determine whether it conforms to planned arrangements, ISO 27001 requirements, and organizational policies. This subclause requires organizations to establish and maintain an internal audit program. Internal audits should be conducted at planned intervals to assess the effectiveness of the ISMS, identify non-conformities, and ensure compliance with applicable requirements. The results of the internal audits help in identifying areas for improvement and taking corrective actions.
Management review: Management review involves a systematic evaluation of the ISMS by top management to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy, effectiveness, and alignment with the organization’s strategic direction. This subclause requires organizations to conduct regular management reviews of the ISMS. Management reviews should assess the performance of the ISMS, review the results of internal audits and other evaluations, identify opportunities for improvement, and make decisions related to resource allocation, improvement initiatives, and policy updates.
By addressing the requirements of Clause 9, organizations can ensure the ongoing effectiveness and improvement of the ISMS. Internal audits help in identifying gaps and non-conformities, while management reviews provide a holistic view of the ISMS’s performance and alignment with organizational objectives. These processes enable organizations to continuously evaluate their information security practices, implement corrective actions, and drive continual improvement, resulting in a more robust and resilient information security management system.
Clause 10: Improvement
Clause 10 of ISO 27001 focuses on the continual improvement of an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It covers general requirements, nonconformity and corrective action, and the importance of ongoing improvement. Let’s explore each subclause:
General: This subclause emphasizes the importance of continually improving the effectiveness of the ISMS. It highlights the need for organizations to establish a culture of continual improvement, where the ISMS is regularly reviewed and enhanced to address changing circumstances, emerging risks, and new technologies. The general requirements include setting objectives for continual improvement, providing resources to support improvement initiatives, and promoting a proactive approach to identifying improvement opportunities.
Nonconformity and corrective action: Nonconformities refer to instances where the ISMS does not meet the requirements of ISO 27001 or the organization’s own policies and procedures. This subclause requires organizations to establish processes for identifying, documenting, and addressing nonconformities. It also emphasizes the importance of taking corrective actions to address the root causes of nonconformities and prevent their recurrence. Corrective actions should be implemented in a timely manner, and their effectiveness should be evaluated.
Continual improvement: Continual improvement is a fundamental principle of ISO 27001. This subclause requires organizations to establish processes for continually improving the suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness of the ISMS. It encourages organizations to seek opportunities for improvement, whether through proactive risk management, lessons learned from incidents, feedback from stakeholders, or advancements in technology. Organizations should evaluate the results of improvement initiatives and take actions to ensure ongoing enhancement of the ISMS.
By addressing the requirements of Clause 10, organizations can foster a culture of continual improvement within their ISMS. This includes identifying and addressing nonconformities, implementing corrective actions, and seeking opportunities for enhancement. Through a proactive approach to improvement, organizations can adapt to changing security risks, enhance their information security practices, and maintain the effectiveness of the ISMS in protecting valuable information assets.
IMPLEMENTATION & CERTICIFATION
mplementation and certification of ISO 27001 involves several key steps to establish and demonstrate compliance with the standard. Here is an overview of the implementation and certification process:
- Understand the Standard: Familiarize yourself with the requirements and guidelines outlined in ISO 27001. Gain a thorough understanding of the standard’s framework, controls, and best practices for information security management.
- Gap Analysis: Conduct a gap analysis to assess your organization’s current information security practices against the requirements of ISO 27001. Identify areas where your organization already meets the standard and areas that require improvement or additional controls.
- Establish an ISMS: Develop and implement an Information Security Management System (ISMS) based on ISO 27001 requirements. This involves defining policies, procedures, and controls to address information security risks, protect assets, and ensure compliance.
- Risk Assessment and Treatment: Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify and evaluate information security risks to your organization’s assets. Develop a risk treatment plan to mitigate or address identified risks effectively. Implement controls and measures to manage and reduce risks to an acceptable level.
- Training and Awareness: Ensure that employees at all levels of the organization receive appropriate training and awareness regarding information security policies, procedures, and their roles and responsibilities in maintaining the security of information assets.
- Documentation: Document the ISMS implementation, including policies, procedures, and processes. Maintain a set of relevant records to demonstrate adherence to the standard and evidence of continual improvement efforts.
- Internal Audit: Conduct regular internal audits of the ISMS to assess its effectiveness, identify non-conformities, and determine opportunities for improvement. Internal audits help evaluate the compliance of your ISMS with ISO 27001 requirements.
- Management Review: Conduct periodic management reviews to evaluate the overall performance of the ISMS. Review the results of internal audits, assess the effectiveness of controls, and make informed decisions for continual improvement.
- Certification Audit: Engage an accredited certification body to perform an independent certification audit of your ISMS. The certification audit involves a thorough evaluation of your organization’s compliance with ISO 27001 requirements and the effectiveness of your ISMS implementation.
- Certification Maintenance: Maintain your ISO 27001 certification by conducting regular surveillance audits as required by the certification body. Continually monitor and improve your ISMS to ensure ongoing compliance and effectiveness.
Obtaining ISO 27001 certification demonstrates your organization’s commitment to information security management and provides assurance to stakeholders that you have implemented effective controls and practices. It can enhance your reputation, instill confidence in customers and partners, and provide a competitive advantage in the market.

ISO 27001 mandatory documents
ISO 27001 requires the implementation of various mandatory documents to establish an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS). While the specific documentation needs may vary depending on the organization’s size, complexity, and industry, the following are some key mandatory documents typically required:
- Information Security Policy: This document outlines the organization’s commitment to information security and provides high-level guidance and direction for the ISMS. It defines the organization’s overall approach to information security and sets the context for implementing controls and managing risks.
- Statement of Applicability (SoA): The SoA identifies the control objectives and controls selected for implementation based on the organization’s risk assessment. It specifies which controls from Annex A of ISO 27001 are applicable and how they are implemented within the organization.
- Risk Assessment Methodology: This document describes the methodology used to assess information security risks within the organization. It outlines the approach for identifying assets, assessing threats and vulnerabilities, determining risk levels, and evaluating the effectiveness of existing controls.
- Risk Treatment Plan: The risk treatment plan details the actions and measures to be taken to treat and mitigate identified risks. It specifies the treatment options, responsibilities, timelines, and resources required for implementing controls and reducing the risk levels to an acceptable level.
- Procedures and Work Instructions: These documents provide step-by-step instructions for implementing specific information security controls or processes. They outline the methods, responsibilities, and actions required to carry out activities such as incident management, access control, asset management, and change management.
- Records and Documentation Control: A documented process for controlling and managing records and documentation related to the ISMS is required. This includes procedures for document approval, version control, distribution, retention, and disposal of records and documents.
- Internal Audit Procedure: This document describes the process for conducting internal audits of the ISMS. It outlines the audit scope, frequency, responsibilities, and criteria for selecting auditors. The procedure should also specify how non-conformities are identified, documented, and addressed.
- Management Review Procedure: The management review procedure outlines the process for top management to review the performance and effectiveness of the ISMS. It specifies the frequency of reviews, the inputs required, the attendees, and the actions to be taken based on the review outcomes.
- Incident Response Plan: An incident response plan documents the organization’s approach to handling and responding to information security incidents. It provides guidelines for incident detection, reporting, assessment, response, containment, recovery, and lessons learned.
- Training and Awareness Program: A documented training and awareness program ensures that employees receive appropriate education and awareness on information security policies, procedures, and their roles in maintaining security. It outlines the training needs, methods, and frequency of training sessions.
These are some of the key mandatory documents required for ISO 27001 compliance. However, it’s important to note that the specific documentation requirements may vary based on the organization’s context and risk profile. It is recommended to refer to ISO 27001:2013 standard and seek guidance from experts or consultants to ensure compliance with the requirements.
ISO 27001 and risk management
ISO 27001 and risk management go hand in hand. ISO 27001 provides a framework for implementing an Information Security Management System (ISMS), while risk management is a critical component of the ISMS. Let’s explore the relationship between ISO 27001 and risk management:
- Risk Assessment: ISO 27001 requires organizations to conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify and evaluate information security risks to their assets. The risk assessment process involves identifying assets, assessing threats and vulnerabilities, and determining the potential impact and likelihood of risks. This helps organizations prioritize and focus their efforts on managing the most significant risks to their information assets.
- Risk Treatment: Once risks are identified and assessed, ISO 27001 requires organizations to develop and implement a risk treatment plan. This plan outlines the actions and measures to be taken to treat and mitigate identified risks. It involves the selection and implementation of appropriate controls to reduce the risks to an acceptable level. The risk treatment plan should consider the organization’s risk appetite, business objectives, legal and regulatory requirements, and other relevant factors.
- Control Selection: ISO 27001 provides a set of controls in Annex A that organizations can choose from to address information security risks. These controls cover various aspects of information security, including access control, physical security, incident management, business continuity, and more. Organizations should select and implement controls based on their risk assessment and risk treatment plan. The controls help organizations manage risks and establish a robust security posture.
- Risk Monitoring and Review: ISO 27001 emphasizes the importance of continually monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of the implemented controls and the overall risk management process. Organizations need to regularly assess the performance of the controls, evaluate changes in the risk landscape, and review the risk treatment plan to ensure its ongoing suitability and effectiveness. This enables organizations to adapt their security measures to emerging threats and changes in their business environment.
- Continuous Improvement: ISO 27001 promotes a culture of continual improvement in risk management. Organizations should continuously evaluate their risk management practices, learn from incidents and near-misses, and seek opportunities to enhance their information security posture. This includes conducting regular risk assessments, refining the risk treatment plan, and implementing lessons learned from incidents and audits.
By integrating risk management practices within the framework of ISO 27001, organizations can establish a proactive approach to identifying, assessing, and managing information security risks. This helps organizations protect their valuable information assets, ensure business continuity, and comply with legal and regulatory requirements. The risk management process also enables organizations to demonstrate due diligence and provides a basis for informed decision-making in managing information security risks effectivel.
What is “ISO 27001 certified”?
“ISO 27001 certified” refers to the achievement of a formal certification that validates an organization’s compliance with the requirements of the ISO/IEC 27001 standard. ISO/IEC 27001 is an internationally recognized standard for information security management systems (ISMS).
To become ISO 27001 certified, an organization undergoes a comprehensive audit process conducted by an accredited certification body. The certification process typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The organization prepares its information security management system (ISMS) based on the requirements of ISO 27001. This involves establishing policies, procedures, controls, and processes to address information security risks and comply with the standard.
- Internal Audit: The organization conducts an internal audit to assess the effectiveness of its ISMS and identify any gaps or areas for improvement. This helps ensure that the organization is ready for the external certification audit.
- Certification Audit: An accredited certification body performs an external audit to assess the organization’s compliance with ISO 27001. The certification audit includes a thorough review of the organization’s ISMS documentation, processes, and practices. The auditor evaluates the implementation of controls, risk management, documentation, and overall adherence to ISO 27001 requirements.
- Corrective Actions: If any non-conformities or areas for improvement are identified during the certification audit, the organization is required to address them through corrective actions. These actions involve resolving non-compliant issues, improving processes, or implementing additional controls as needed.
- Certification Decision: Based on the findings of the certification audit and the successful completion of any corrective actions, the certification body makes a decision regarding the certification. If the organization demonstrates compliance with ISO 27001 requirements, it is awarded the ISO 27001 certification.
- Surveillance Audits: After obtaining the initial certification, the organization is subject to periodic surveillance audits by the certification body. These audits are conducted at regular intervals to ensure that the organization maintains compliance with ISO 27001 over time.
What is the current ISO 27001 standard?
By achieving ISO 27001 certification, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to information security, compliance with industry best practices, and ability to effectively manage information security risks. The certification provides confidence to customers, partners, and stakeholders that the organization has implemented a robust information security management system in accordance with international standards.
The current ISO 27001 standard is ISO/IEC 27001:2022. It is the latest version of the standard for information security management systems (ISMS) developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an ISMS within the context of an organization. It provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive information, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
It’s important to note that standards are periodically reviewed and updated to reflect the evolving landscape of technology, security threats, and best practices.
What is ISO 27001 information security management?
ISO 27001 is an international standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). It provides a framework for organizations to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve their information security management practices.
Information security management refers to the systematic approach and processes that organizations implement to protect their sensitive information assets from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, destruction, and disruption. It involves identifying and managing information security risks, implementing controls and safeguards, and ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
The ISO 27001 standard sets out a comprehensive set of requirements and best practices for establishing an effective ISMS. It provides guidance for organizations to assess their information security risks, select and implement appropriate controls, and monitor and manage their security posture. The standard encompasses a wide range of areas related to information security, including:
- Risk assessment and management: Identifying and evaluating information security risks, and implementing measures to mitigate or treat those risks.
- Security policy: Developing and maintaining an information security policy that sets out the organization’s commitment to information security and its objectives.
- Organizational context: Understanding the organization’s internal and external context, including its stakeholders, industry, legal and regulatory requirements, and business environment.
- Security controls: Implementing a comprehensive set of information security controls to address various aspects of information security, such as access control, asset management, incident response, business continuity, and more.
- Incident management: Establishing processes and procedures to detect, respond to, and recover from information security incidents.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly reviewing and improving the effectiveness of the ISMS through monitoring, measurement, internal audits, management reviews, and corrective actions.
By implementing ISO 27001 information security management practices, organizations can establish a systematic and proactive approach to protecting their sensitive information assets. It helps organizations build trust with stakeholders, demonstrate compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, and mitigate the risks associated with information security breaches.
What are the ISO 27000 standards ?
The ISO 27000 series is a collection of international standards and guidelines related to information security management systems (ISMS). These standards are developed and published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). The ISO 27000 series provides a comprehensive framework for organizations to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve their information security practices. Here are some key standards within the ISO 27000 series:
- ISO/IEC 27001:2013 – Information Security Management Systems – Requirements: This is the core standard for establishing an ISMS. It sets out the requirements for organizations to implement an information security management system based on a risk management approach.
- ISO/IEC 27002:2013 – Code of Practice for Information Security Controls: This standard provides a comprehensive set of information security controls and best practices. It offers guidance on the selection, implementation, and management of controls across various domains of information security.
- ISO/IEC 27003:2017 – Information Security Management System Implementation Guidance: This standard provides practical guidance on implementing an ISMS based on ISO 27001. It offers recommendations for planning, establishing, operating, monitoring, reviewing, maintaining, and improving an ISMS.
- ISO/IEC 27004:2016 – Information Security Management – Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis, and Evaluation: This standard focuses on monitoring, measuring, analyzing, and evaluating the performance and effectiveness of an ISMS. It provides guidance on establishing metrics, collecting data, analyzing results, and reporting on the performance of information security controls and processes.
- ISO/IEC 27005:2018 – Information Security Risk Management: This standard provides guidelines for organizations to establish and maintain a systematic approach to information security risk management. It offers guidance on risk assessment, risk treatment, and the selection and implementation of appropriate controls.
- ISO/IEC 27006:2015 – Requirements for Bodies Providing Audit and Certification of Information Security Management Systems: This standard specifies the requirements for certification bodies that conduct audits and issue certifications for ISMS based on ISO 27001. It outlines the criteria for the competence, independence, and impartiality of certification bodies.
These standards within the ISO 27000 series provide organizations with a comprehensive framework, best practices, and guidelines for establishing and managing effective information security management systems.
ISO 27001 supporting standards
The ISO 27001 standard is supported by several other standards within the ISO 27000 series. These supporting standards provide additional guidance and frameworks to enhance information security management practices. Here are some key supporting standards related to ISO 27001:
- ISO/IEC 27002:2013 – Code of Practice for Information Security Controls: This standard provides a comprehensive set of information security controls and best practices. It offers guidance on the selection, implementation, and management of controls across various domains of information security.
- ISO/IEC 27003:2017 – Information Security Management System Implementation Guidance: This standard provides practical guidance on implementing an ISMS based on ISO 27001. It offers recommendations for planning, establishing, operating, monitoring, reviewing, maintaining, and improving an ISMS.
- ISO/IEC 27004:2016 – Information Security Management – Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis, and Evaluation: This standard focuses on monitoring, measuring, analyzing, and evaluating the performance and effectiveness of an ISMS. It provides guidance on establishing metrics, collecting data, analyzing results, and reporting on the performance of information security controls and processes.
- ISO/IEC 27005:2018 – Information Security Risk Management: This standard provides guidelines for organizations to establish and maintain a systematic approach to information security risk management. It offers guidance on risk assessment, risk treatment, and the selection and implementation of appropriate controls.
- ISO/IEC 27006:2015 – Requirements for Bodies Providing Audit and Certification of Information Security Management Systems: This standard specifies the requirements for certification bodies that conduct audits and issue certifications for ISMS based on ISO 27001. It outlines the criteria for the competence, independence, and impartiality of certification bodies.
These supporting standards complement ISO 27001 by providing detailed guidance, best practices, and specific frameworks for different aspects of information security management. They can help organizations enhance their implementation and management of an ISMS, address specific information security concerns, and ensure compliance with international standards and best practices.

Conclusion
Frequently Asked Question:
What is ISO 27001 certification, and why is it important for businesses in Nepal?
ISO 27001 is an internationally recognized standard that sets requirements for an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Achieving ISO 27001 certification demonstrates an organization’s commitment to securing sensitive data and managing information risks effectively.
In Nepal, businesses face increasing cyber threats and data breaches, making information security a critical concern. ISO 27001 certification is crucial for businesses as it helps them establish a robust information security framework, identify and address potential vulnerabilities, and safeguard valuable information from unauthorized access and cyberattacks. Additionally, ISO 27001 certification enhances the company’s reputation, improves customer confidence, and can lead to a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
How does the ISO 27001 certification process work in Nepal?
The ISO 27001 certification process in Nepal involves the following steps:
- Gap Analysis: The certification journey begins with a gap analysis, where the current information security practices and processes are assessed against the requirements of ISO 27001.
- Policy and Procedure Development: Based on the gap analysis, an organization develops policies, procedures, and controls to meet ISO 27001 standards.
- Implementation: The organization implements the ISMS, ensuring that information security measures are integrated into their operations.
- Internal Audit: An internal audit is conducted to assess the effectiveness of the ISMS and identify any non-conformities that need to be addressed.
- Management Review: Senior management reviews the internal audit results and implements corrective actions to rectify identified issues.
- Certification Body Selection: The organization chooses an accredited certification body to conduct an external audit.
- External Audit: The chosen certification body performs an external audit to evaluate the organization’s compliance with ISO 27001 requirements.
- Certification Issuance: If the organization meets all the ISO 27001 criteria, the certification body issues the ISO 27001 certificate.
How long does it typically take for a business to get ISO 27001 certified in Nepal?
Answer: The duration to obtain ISO 27001 certification can vary depending on the size and complexity of the organization, its current information security practices, and its commitment to meeting ISO 27001 requirements. On average, the certification process may take anywhere from 6 to 12 months.
Is ISO 27001 certification a one-time process, or do businesses need to renew it periodically?
ISO 27001 certification is not a one-time event. It is valid for a specific period, usually three years, after which the organization must undergo a re-certification audit to maintain its certified status. During the three-year period, businesses must conduct regular surveillance audits to ensure ongoing compliance with ISO 27001 standards.
How can ISO 27001 certification benefit businesses in Nepal beyond enhancing information security?
ISO 27001 certification offers several additional benefits to businesses in Nepal, including:
- Increased Customer Trust: Certified organizations demonstrate a commitment to protecting customer information, fostering trust and loyalty among clients.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: ISO 27001 helps businesses comply with relevant data protection and privacy laws in Nepal and other international jurisdictions.
- Business Expansion Opportunities: ISO 27001 certification can open doors to new markets and business opportunities, especially when dealing with partners or clients who require strong information security practices.
- Improved Efficiency: The implementation of an ISMS streamlines processes, reduces security incidents, and improves overall operational efficiency.
- Risk Management: ISO 27001 assists businesses in identifying and mitigating information security risks effectively.
- Employee Confidence: Employees feel more secure and motivated knowing their organization takes information security seriously.
How can businesses in Nepal get started with ISO 27001 certification?
To begin the ISO 27001 certification process, businesses in Nepal can follow steps:
- Information Gathering: Conduct research on ISO 27001 and its requirements to understand the standard’s scope and benefits.
- Commitment from Top Management: Gain support from senior management to ensure the organization’s commitment to implementing an ISMS.
- Engage an Expert: Consider seeking assistance from an experienced ISO certification consultant or company like “Quality Management System in Nepal Pvt. Ltd.” They can guide you through the process efficiently.
- Gap Analysis: Conduct a thorough evaluation of existing information security practices against ISO 27001 requirements to identify gaps.
- ISMS Development: Develop and implement policies, procedures, and controls based on the gap analysis.
- Training and Awareness: Provide necessary training to employees to raise awareness about information security best practices.
- Internal Audit: Perform an internal audit to assess the effectiveness of the ISMS.
- External Audit: Engage an accredited certification body to conduct the final external audit.
- Certification: If the organization meets all the requirements, the ISO 27001 certificate will be issued.
What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is an international standard for Information Security Management System (ISMS). It provides a systematic approach for organizations to manage and protect their sensitive information, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
How to do risk assessment for ISO 27001?
To perform a risk assessment for ISO 27001, follow these steps: a. Identify assets: List all the valuable information and IT assets in your organization. b. Identify threats: Identify potential threats or events that could harm these assets. c. Assess vulnerabilities: Determine weaknesses or vulnerabilities that could be exploited by threats. d. Evaluate risks: Assess the likelihood and impact of each risk by combining the threat and vulnerability levels. e. Implement controls: Develop and implement security controls to mitigate identified risks. f. Review and update: Regularly review and update the risk assessment to address emerging threats and changes in your organization’s environment.
In order to maintain a seamless and efficient ISO certification process, partnering with a trusted ISO consultant is crucial. At Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd., we are committed to providing your organization with expert guidance and support, ensuring a cost-effective and successful ISO implementation journey. As the leading ISO System Certification body in Nepal, we offer a comprehensive range of certification services tailored to your organization’s needs.
Explore our range of ISO certification services:
- ISO 55001 Certification in Nepal: Enhance asset management and energy efficiency.
- TL 9000 Certification in Nepal: Elevate quality standards in the telecommunications industry.
- IATF 16949 Certification in Nepal: Elevate automotive quality and meet industry requirements.
- ISO 37001 Certification in Nepal: Strengthen anti-bribery management systems.
- AS 9001 Certification in Nepal: Attain aerospace quality standards for excellence.
- ISO FSSC 22000 Certification in Nepal: Ensure safe and quality food production.
- ISO 29990 Certification in Nepal: Elevate training and learning services.
- ISO SA 8000 Certification in Nepal: Prioritize social accountability and ethical practices.
- ISO 27017 Certification in Nepal: Ensure secure cloud computing environments.
- ISO 20000-1:2018 Certification in Nepal: Elevate IT service management systems.
- ISO 22301 Certification in Nepal: Enhance business continuity and resilience.
- ISO 41001 Certification in Nepal: Optimize facility management systems.
- HACCP Certification in Nepal: Ensure food safety and hazard analysis.
- ISO 50001 Certification in Nepal: Enhance energy management and efficiency.
- ISO 13485 Certification in Nepal: Elevate medical device quality standards.
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Certification in Nepal: Ensure quality and compliance in manufacturing.
- ISO 9001 Certification in Nepal: Elevate overall quality management.
- ISO 15189:2022 Certification for Medical Laboratories in Nepal: Elevate medical laboratory practices.
- ISO 17025 Certification for Testing and Calibration Laboratories in Nepal: Ensure accurate testing and calibration.
- ISO 27001:2022 Certification for Information Security in Nepal: Enhance information security practices.
- ISO 22000 Certification for Food Safety Management System in Nepal: Ensure safe and quality food production.
- ISO 45001:2018 Certification for Occupational Health and Safety in Nepal: Elevate health and safety standards.
- ISO 14001:2015 Certification for Environmental Management in Nepal: Enhance environmental sustainability.
Our dedicated team is ready to provide your organization with customized solutions and expert assistance. If you have any queries or are ready to embark on your ISO certification journey, feel free to contact us at 9840525565 for a free consultation on our ISO certification services. Trust Quality Management System Nepal Pvt. Ltd. to be your partner in achieving excellence and compliance.
