Table of Contents
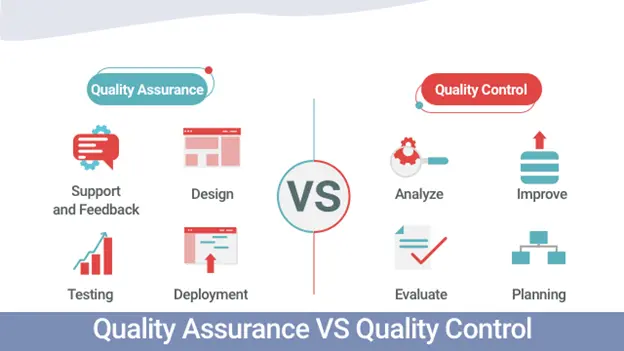
what is Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control?
Meeting customer expectations is the ultimate goal of any business. Quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) are essential tools to achieve this goal. QA involves proactive measures throughout the development process, ensuring products and services are built to the right specifications. QC plays a complementary role, focusing on catching any defects that slip through the cracks before the product reaches the customer.
What is Quality Assurance (QA)?
Quality Assurance (QA) encompasses the proactive processes and systematic activities implemented to prevent quality defects in a product or service. QA’s core focus lies in establishing standards and methodologies to ensure that processes are followed consistently and effectively throughout the development lifecycle.
Key Elements of Quality Assurance:
- Process Definition: Developing clear procedures and standards outlining how a product or service should be produced.
- Documentation: Creating thorough records of processes, testing, and any issues encountered to maintain traceability and allow for audits.
- Audits: Conducting regular evaluations and internal reviews to confirm adherence to standards and identify process improvement areas.
- Training: Providing comprehensive training to staff on quality standards and procedures to ensure consistent implementation across teams.
- Supplier Management: Establishing quality requirements and conducting audits to ensure that external suppliers also meet necessary standards.
What is Quality Control (QC)?
Quality Control (QC) is a reactive process that centers upon detecting and fixing product or service defects before they reach the customer. QC usually involves various testing and inspection activities to verify conformance to quality specifications.
Key Elements of Quality Control:
- Testing: Executing a range of tests (e.g., functional tests, performance tests, usability tests) on products or services to discover potential problems.
- Inspection: Examining raw materials, components, and finished products to assess their quality and conformance to standards.
- Statistical Sampling: Utilizing statistical methods to inspect a representative sample of products rather than the entire output.
- Corrective Action: When defects are uncovered, taking steps to address the root cause and rectify the issue to prevent recurrence.
- Reporting: Documenting inspection results, defects found, and corrective actions taken.
Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control: The Key Differences
While Quality Assurance and Quality Control are crucial facets of quality management, they have distinct focuses. Here’s a breakdown of the primary differences:
| Characteristic | Quality Assurance | Quality Control |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Process-oriented | Product-oriented |
| Nature | Proactive | Reactive |
| Goal | Defect prevention | Defect identification |
| Timing | Across the entire development lifecycle | Typically at the end of production or before release |
| Scope | Broader | More focused on a specific product or deliverable |
Imagine building a house. Quality assurance (QA) is akin to having a detailed blueprint and hiring skilled architects – it sets the foundation for a well-constructed structure. Quality control (QC) is like the careful inspection before move-in day – finding any imperfections that need fixing. Both are vital for ensuring the final house is both built correctly and free from defects.
How Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control Work Together?
QA and QC function in a complementary manner, forming a robust quality management system:
- Process Design: QA lays the foundation by establishing clear quality standards and procedures.
- Product Development: Products or services are developed in accordance with the defined QA processes.
- Quality Control Testing: QC conducts inspections and testing to detect any deviations from the established quality standards.
- Corrective Action and Feedback: When defects are found by QC, processes are reviewed and potentially adjusted within the QA framework to prevent recurrence.
Examples of Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control in Different Industries
- Software Development
- QA: Defining code review standards, setting up automated testing frameworks.
- QC: Conducting manual and automated tests to find bugs.
- Manufacturing
- QA: Implementing statistical process control and quality audits
- QC: Product inspections, raw material testing
- Healthcare
- QA: Documenting patient care protocols, staff training procedures
- QC: Chart reviews to ensure standard operating procedures are followed
The Benefits of Effective Quality Assurance Vs. Quality Control
Robust QA and QC practices offer an array of benefits for organizations:
- Enhanced Product/Service Quality: Ensures products and services meet customer expectations.
- Reduced Costs: Preventing defects saves resources needed for rework and addressing customer complaints.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Consistent quality builds trust and loyalty.
- Improved Efficiency: Well-defined Quality Assurance processes streamline production and reduce waste.
- Competitive Advantage: A reputation for quality sets businesses apart.
Conclusion of Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control
Understanding the distinction between Quality Assurance vs. Quality Control is essential for achieving exceptional product or service quality. By establishing strong Quality Assurance processes and robust Quality Control activities, organizations can consistently deliver on their promises and exceed customer expectations.
Are you looking to strengthen your quality management practices? Contact us for expert Quality Assurance and Quality Control consultancy services!
Frequently Asked Questions:
What’s the difference between quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC)?
QA is proactive, focusing on preventing defects throughout the process. QC is reactive, focused on identifying defects in the finished product or service.
Can you give examples of QA and QC in action?
Sure! In software development, QA involves setting code review standards, while QC means conducting tests to find bugs.
Why are both QA and QC important?
They work together! QA sets the standards, and QC checks if those standards are met. This combined approach ensures high-quality, defect-free products and services.
What benefits do businesses see from strong QA and QC?
Many! They include improved product quality, cost savings from defect prevention, increased customer satisfaction, streamlined operations, and a boosted competitive edge.
Does the size of my business matter for implementing QA and QC?
No! Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, quality assurance and quality control principles can be adapted to suit your needs and bring significant value.